Introduction
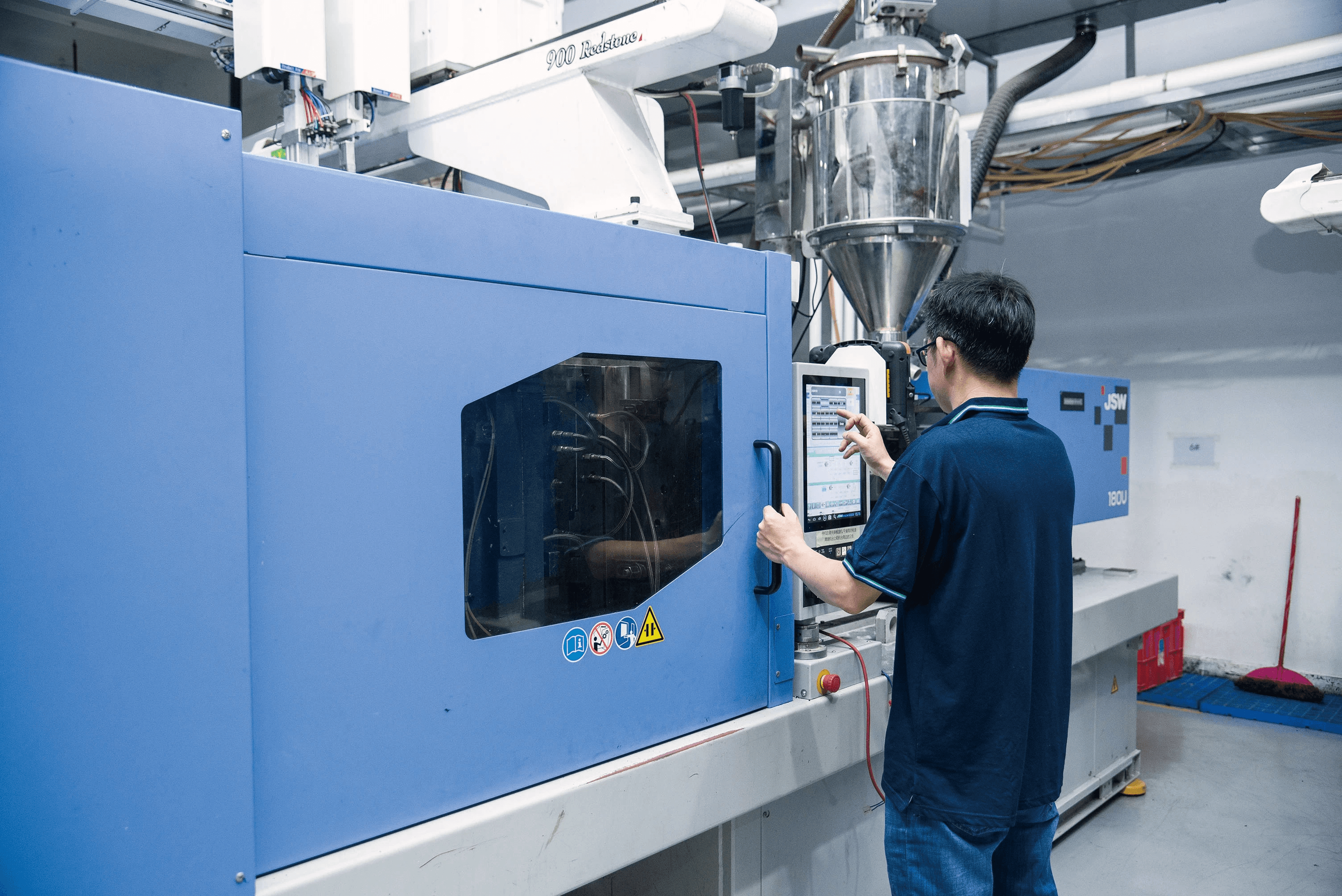
In the world of manufacturing, high pressure injection molding stands out as a crucial technique for producing complex plastic parts with precision and efficiency. Understanding how pressure works in this process is essential for manufacturers aiming to optimize their operations and achieve superior product quality. From the basic principles of pressure control to the nuances of high pressure injection molding, this introduction sets the stage for exploring its significance in modern production.
Understanding Pressure in Injection Molding
Pressure is a fundamental aspect of injection molding, influencing every stage from material melting to final part ejection. In high pressure injection molding, the force applied during the injection process can significantly affect both cycle times and product integrity. By grasping what constitutes effective pressure management, manufacturers can better navigate challenges such as material flow and mold filling.
The Importance of Pressure Control
Effective pressure control is paramount in ensuring that molded parts meet stringent quality standards while minimizing waste and production costs. Too much or too little pressure can lead to defects such as warping or incomplete filling, which ultimately compromise product performance. Therefore, understanding how does pressure affect injection molding is key for manufacturers looking to maintain consistency and reliability in their output.
Overview of High Pressure Injection Molding
High pressure injection molding refers to a specialized technique where molten plastic is injected into molds at elevated pressures, typically ranging from 60 MPa to over 200 MPa depending on the application. This method allows for intricate designs and tight tolerances that other methods may struggle to achieve. With insights into what is the difference between low pressure and high pressure injection molding, we can appreciate why many industries are gravitating towards this advanced manufacturing solution.
The Science Behind High Pressure Injection Molding
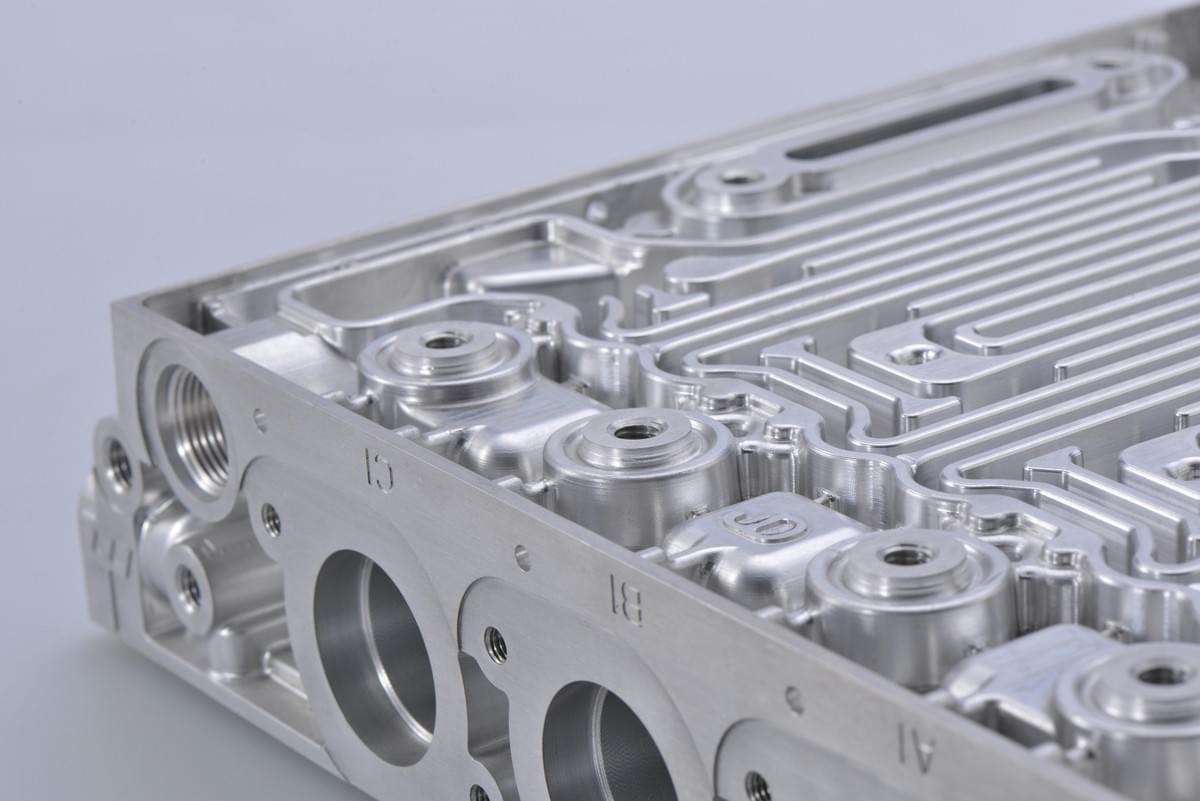

High pressure injection molding is a fascinating process that transforms raw materials into intricately designed products with precision and efficiency. This method utilizes elevated pressure to inject molten plastic into molds, ensuring that every nook and cranny of the mold is filled accurately. Understanding the science behind high pressure injection molding not only highlights its significance in manufacturing but also sets it apart from other molding techniques.
What is High Pressure Injection Molding?
High pressure injection molding refers to the technique where molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure, typically exceeding 1000 bar (or approximately 100 MPa). This process allows for the creation of complex shapes and fine details, which are often challenging to achieve with low pressure methods. The primary goal of high pressure injection molding is to ensure consistent quality and dimensional accuracy across large production runs, making it ideal for industries requiring precision-engineered components.
How High Pressure Molding Works
The process of high pressure molding involves several key steps: first, raw plastic granules are heated until they melt; next, this molten material is forced into a mold using a screw or plunger mechanism at high pressures. Once the material fills the mold cavity, it cools and solidifies before being ejected as a finished part. Understanding how does pressure affect injection molding is crucial because higher pressures help eliminate voids and air pockets within the molded product, resulting in superior strength and durability.
Key Benefits of High Pressure Injection Molding
The advantages of high pressure injection molding are numerous and significant. For starters, this method allows for faster cycle times compared to low-pressure alternatives, which can be crucial for meeting market demands efficiently. Additionally, products manufactured through this technique often exhibit enhanced mechanical properties due to better material flow and reduced defects—making it an attractive option for businesses looking to optimize their production processes while ensuring quality.
What is the Difference Between Low Pressure and High Pressure Injection Molding?

When it comes to injection molding, understanding the difference between low pressure and high pressure injection molding is crucial for manufacturers and product developers alike. While both methods aim to create high-quality parts, they differ significantly in their processes, applications, and material compatibility. This section will delve into these differences to help clarify which method might be best suited for your specific needs.
Definitions and Applications
Low pressure injection molding typically operates at pressures below 1000 psi (approximately 7 MPa), making it ideal for creating lightweight components with less stress on materials. This method is often employed in industries where delicate parts are required, such as in automotive interiors or consumer electronics. On the other hand, high pressure injection molding operates at much higher pressures—usually above 3000 psi (around 20 MPa)—which allows for denser materials and more complex geometries.
The process of high pressure moulding excels in producing robust products that demand precision and durability. Industries such as medical device manufacturing, aerospace, and heavy machinery frequently rely on high pressure injection molding due to its ability to handle a wide variety of thermoplastics and thermosetting resins effectively. Consequently, knowing what is the difference between low pressure and high pressure injection molding can guide you toward selecting the right technique based on your project's requirements.
Material Considerations
Material selection plays a pivotal role when determining whether to use low or high pressure injection molding techniques. Low pressure processes generally utilize softer materials that can easily flow into molds without risking damage from excessive force. This makes them suitable for applications requiring flexibility but limits their use with more rigid plastics.
In contrast, high pressure injection molding accommodates a broader range of materials—including those that are more viscous or require precise detailing—thanks to its ability to exert significant force during production. This versatility allows manufacturers to create intricate designs while ensuring optimal material properties like strength and durability are achieved. When considering how does pressure affect injection molding? The answer lies significantly in how well each method can manage different types of materials under varying conditions.
Cost Implications
Cost considerations are always top-of-mind for manufacturers when choosing between low and high pressure methods; however, it's essential not just to look at initial expenses but also long-term implications. Low pressure systems often have lower upfront costs due to simpler machinery requirements but may incur higher operational costs if production speeds lag behind those achievable with high-pressure systems.
High-pressure equipment tends toward a steeper initial investment due to complex machinery capable of sustaining elevated pressures—however, this investment pays off through faster cycle times and improved part quality over time. Ultimately, understanding what is the process of high-pressure moulding can help businesses make informed decisions about balancing cost against quality demands while maximizing efficiency across their operations.
How Does Pressure Affect Injection Molding?
Pressure plays a pivotal role in the injection molding process, influencing everything from cycle time to product quality. Understanding how pressure interacts with various elements of molding is essential for manufacturers aiming to optimize their operations. In this section, we will delve into the impact of pressure on cycle time, the effects on product quality, and the importance of balancing pressure for optimal results.
The Impact of Pressure on Cycle Time
Cycle time is a critical factor in high pressure injection molding as it directly affects production efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Higher pressures can lead to faster filling of molds, which reduces overall cycle time significantly; however, this must be balanced with other factors like cooling times and material characteristics. In contrast, lower pressure settings may result in longer cycle times due to slower filling rates and potential issues with incomplete mold fills—this highlights what is the difference between low pressure and high pressure injection molding?
Moreover, understanding what is the process of high pressure moulding helps in optimizing cycle times further. By adjusting parameters such as injection speed and hold pressures, manufacturers can fine-tune their processes to achieve faster production rates without compromising on quality. Ultimately, effective management of pressure not only enhances productivity but also ensures that resources are utilized efficiently.
Pressure Effects on Product Quality
The relationship between pressure and product quality in high pressure injection molding cannot be overstated. High pressures generally lead to better material flow within molds, which facilitates more uniform filling and reduces defects such as voids or sink marks—issues that are more prevalent at lower pressures. Additionally, increased packing pressures can help eliminate air entrapment within the molded parts, resulting in stronger final products.
However, it's crucial to recognize that excessive pressure can also introduce challenges; for instance, it may cause warping or dimensional inaccuracies if not controlled properly. This makes it vital for manufacturers to understand how does pressure affect injection molding processes comprehensively so they can maintain optimal conditions throughout production runs. Balancing these variables ensures that products meet stringent quality standards while leveraging the advantages offered by high-pressure systems.
Balancing Pressure for Optimal Results
Finding the sweet spot when it comes to balancing pressure is key for achieving optimal results in high-pressure injection molding processes. Manufacturers must consider various factors including material properties and mold design while determining appropriate pressures—what is the pressure MPa for injection molding varies based on these considerations too! Striking a balance allows producers to maximize efficiency while minimizing waste or defects.
Furthermore, collaboration with experienced high-pressure injection molding manufacturers can provide valuable insights into best practices for managing pressures effectively throughout production cycles. They often possess data from real-world applications that highlight successful strategies employed across different industries—these insights are invaluable when navigating complex manufacturing environments where precision is paramount.
In summary, understanding how does pressure affect injection molding involves recognizing its influence on both cycle time and product quality while ensuring an effective balance across all parameters involved in production.
What is the Pressure MPa for Injection Molding?

Understanding the pressure requirements in injection molding is crucial for achieving optimal results. Specifically, high pressure injection molding typically operates at pressures ranging from 70 to 150 MPa, depending on various factors such as material type and part complexity. Knowing what is considered standard pressure can help manufacturers fine-tune their processes and ensure product quality.
Standard Pressure Ranges
In high pressure injection molding, the standard pressure ranges can vary significantly based on the application and materials used. For instance, thermoplastics often require pressures between 80 to 120 MPa to achieve ideal flow characteristics and minimize defects. On the other hand, specialized materials like engineering plastics may necessitate even higher pressures, pushing up to 150 MPa or more in some cases.
These standard ranges are not set in stone; they can be influenced by the type of machine used and specific design parameters of the mold itself. When asking What is the difference between low pressure and high pressure injection molding?, it’s essential to note that lower pressures typically range from 20 to 60 MPa, which are suitable for less complex parts or softer materials. As a result, understanding these ranges helps manufacturers select appropriate machinery and optimize their production processes.
Factors Influencing Pressure Requirements
Several factors influence the required pressure in high pressure injection molding beyond just material choice. One significant factor is part geometry; intricate designs with thin walls generally require higher pressures for proper filling compared to simpler shapes. Additionally, mold temperature plays a vital role—higher temperatures can reduce viscosity but may also lead to increased cycle times if not managed properly.
Another consideration is the type of injection molding machine being used; different machines have varying capabilities regarding maximum achievable pressures. Understanding how does pressure affect injection molding helps manufacturers tailor their processes accordingly—too little pressure might result in incomplete fills or surface imperfections while too much could lead to flash or excessive wear on molds. Thus, balancing these factors ensures efficient production without compromising quality.
Measuring Pressure in Injection Molding
Measuring pressure accurately during high pressure injection molding is essential for maintaining control over the process and ensuring consistency across production runs. Typically, manufacturers utilize sensors installed within machines that provide real-time data regarding cavity fill pressures throughout each cycle phase—this allows immediate adjustments if needed.
Modern systems often feature advanced monitoring technology that can log historical data for analysis over time, helping identify trends or potential issues before they escalate into costly problems down the line. High-pressure injection molding manufacturers frequently employ these systems as part of their quality assurance protocols to ensure every component meets stringent specifications consistently.
By grasping what is the process of high-pressure moulding involves—including precise measurement techniques—manufacturers can enhance productivity while minimizing waste due to defective parts or inefficient cycles.
Insights from High Pressure Injection Molding Manufacturers

When it comes to high pressure injection molding, manufacturers like Baoyuan are at the forefront of innovation and efficiency. Their expertise in this field allows them to produce high-quality components that meet the rigorous demands of various industries. With a focus on precision and reliability, Baoyuan exemplifies what it means to be a leader among high pressure injection molding manufacturers.
Featuring Baoyuan's Expertise
Baoyuan has carved out a niche in the world of high pressure injection molding by leveraging cutting-edge technology and advanced materials. Their team is dedicated to understanding the nuances of what is the process of high pressure moulding, ensuring that every step—from material selection to final inspection—is optimized for performance. By maintaining strict quality control measures, Baoyuan consistently delivers products that not only meet but exceed customer expectations.
One standout feature of Baoyuan's operations is their commitment to research and development, which drives continuous improvement in their processes. They utilize state-of-the-art machinery capable of managing varying pressures, allowing for flexibility in production while adhering to industry standards regarding what is the pressure MPa for injection molding. This adaptability enables them to handle both small-scale projects and large-volume production runs without compromising quality.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
High pressure injection molding finds its applications across diverse sectors such as automotive, consumer goods, and medical devices. For instance, one notable case study involved producing intricate automotive parts that required precise tolerances under high stress conditions—showcasing how does pressure affect injection molding outcomes dramatically influences product integrity. The ability to maintain consistent quality under these demanding conditions highlights why many companies are shifting towards high pressure methods.
Moreover, Baoyuan has successfully partnered with leading brands in developing custom solutions tailored specifically for their unique requirements. These collaborations illustrate not only the versatility of high pressure injection molding but also its cost-effectiveness when compared with low-pressure alternatives—what is the difference between low pressure and high pressure injection molding? In many instances, clients have reported significant reductions in cycle times while enhancing product durability thanks to this method.
Trends in High Pressure Injection Molding
As industries evolve, so do the techniques employed within them; trends indicate an increasing shift towards automation within high pressure injection molding processes. Manufacturers are investing heavily in smart technology that monitors real-time data on how does pressure affect injection molding outcomes throughout production cycles—leading to improved efficiency and reduced waste. This trend reflects a broader movement toward sustainability while still delivering top-notch performance.
Additionally, there’s growing interest in sustainable materials suitable for use within these systems; advancements are being made with bio-based resins that can withstand higher pressures without compromising structural integrity or environmental considerations. As more companies recognize the benefits associated with what is the process of high pressure moulding—including enhanced dimensional accuracy—the demand for innovative solutions continues to rise among high pressure injection molding manufacturers like Baoyuan.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the nuances of high pressure injection molding is crucial for anyone involved in manufacturing processes. This technique not only enhances product quality but also optimizes cycle times, making it a favored choice in various industries. As we’ve explored, the differences between low pressure and high pressure injection molding can significantly impact material selection and overall costs.
Key Takeaways on Injection Molding Pressure
One of the most pivotal aspects of high pressure injection molding is its ability to produce intricate designs with remarkable precision. The process of high pressure moulding requires careful control of parameters to ensure that every component meets stringent quality standards. Additionally, knowing how does pressure affect injection molding can help manufacturers fine-tune their operations for maximum efficiency and output.
Future of High Pressure Injection Molding
Looking ahead, the future of high pressure injection molding appears promising as technology continues to advance. Innovations in machinery and materials are expected to enhance capabilities, allowing for even more complex designs while reducing costs associated with production. Moreover, as industries increasingly prioritize sustainability, manufacturers may explore eco-friendly materials compatible with high pressure processes.
Choosing the Right Manufacturer for Your Needs
When selecting a manufacturer for your high pressure injection molding needs, it’s essential to consider their expertise and track record in the field. High pressure injection molding manufacturers should demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of what is the difference between low pressure and high pressure injection molding to provide tailored solutions that meet specific requirements. Ultimately, aligning with a knowledgeable partner can significantly impact your project’s success.

