Introduction
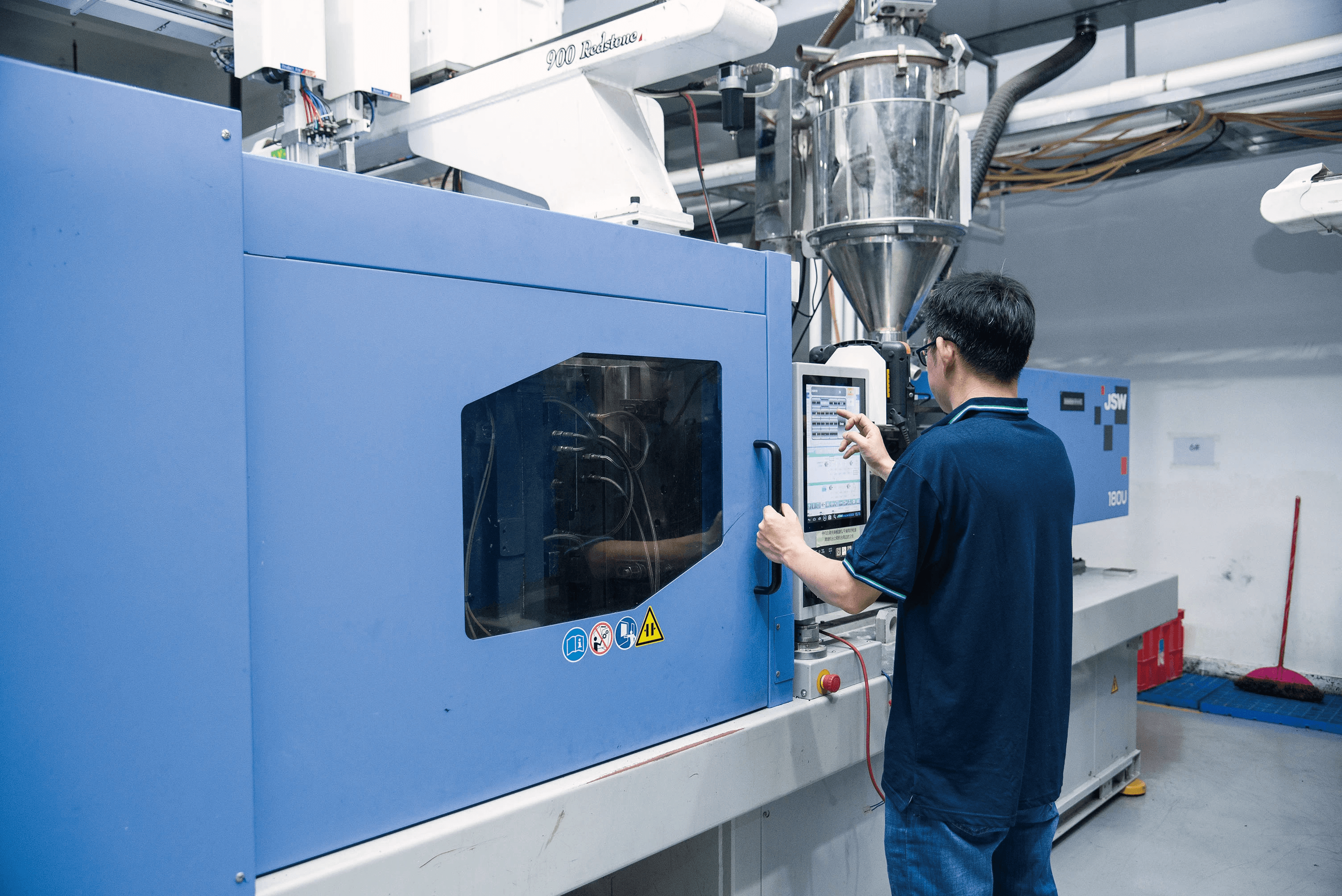
In the world of manufacturing, two processes often take center stage: injection molding and extrusion. While both methods serve the purpose of shaping plastic materials, they each come with unique characteristics and applications that can significantly impact production outcomes. This introduction aims to clarify these differences, helping you navigate the complex landscape of injection molding vs extrusion.
Understanding Injection Molding and Extrusion
Injection molding involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to create intricate shapes and designs. This process is favored for its ability to produce high-precision parts with excellent surface finish and minimal waste. On the other hand, extrusion involves forcing melted plastic through a die to create long continuous shapes like pipes or sheets, making it ideal for specific applications where uniformity is key.
Key Applications of Each Process
When considering injection molding vs extrusion, it's essential to note their respective applications. Injection molding is commonly used for manufacturing components such as automotive parts, consumer goods, and medical devices due to its versatility in creating complex geometries. In contrast, extrusion moulding excels in producing products like tubing, profiles, and films that require consistent cross-sectional shapes over long lengths.
The Cost Factor in Manufacturing Choices
Cost considerations play a pivotal role in deciding between these two processes—Is extrusion better than injection molding? The answer largely depends on factors such as production volume and part complexity. While initial setup costs for injection molding can be higher due to mold creation, it often leads to lower per-unit costs at scale compared to extrusion—highlighting the importance of understanding injection molding vs extrusion cost dynamics before making a choice.
Process Overview
Understanding the intricacies of injection molding and extrusion is essential for making informed manufacturing decisions. Both processes are widely used in the production of plastic components, yet they differ significantly in operation, efficiency, and application. This section will delve into how each process works, highlighting their unique characteristics.
How Injection Molding Works
Injection molding is a highly efficient manufacturing process that involves injecting molten plastic into a pre-designed mold. The material cools and solidifies within the mold to form precise shapes, which can range from intricate designs to simple components. One of the advantages of injection molding is its ability to produce high volumes of identical parts with tight tolerances, making it ideal for mass production.
The process begins with heating plastic pellets until they melt and become a viscous liquid. This liquid is then injected under high pressure into a mold cavity where it takes shape as it cools down. While injection molding can be costly due to initial setup expenses, its speed and precision often make it more economical in large-scale production when compared to extrusion.
Exploring the Extrusion Process
Extrusion is another popular method used for shaping plastics but operates quite differently than injection molding. In this process, plastic material is heated until it becomes soft and pliable before being forced through a die to create long continuous shapes like tubes or sheets. This method allows for consistent cross-sectional profiles over long distances, making it perfect for applications requiring uniformity.
Unlike injection molding's batch approach, extrusion produces materials continuously; once started, the machine keeps running until production stops or changes are made. However, while extrusion provides flexibility in creating various shapes and sizes, its ability to form complex geometries pales in comparison to what injection molding can achieve. Is extrusion better than injection molding? It really depends on your specific needs—each has its strengths.
Key Differences in Operation
When comparing injection molding vs extrusion, several operational differences come into play that influence manufacturing choices significantly. Injection molding typically requires molds that are expensive but yield highly detailed parts quickly; conversely, extrusion relies on dies that are generally simpler but may not achieve the same level of detail found in molded items.
Another key difference lies in the production cycle: while injection molding operates on a batch basis—producing distinct items one at a time—extrusion runs continuously without interruptions once set up correctly. Additionally, understanding what is the difference between extrusion grade and injection grade materials helps manufacturers select appropriate plastics based on their intended application; each processing method has specific material requirements tailored for optimal performance.
In summary, choosing between these two methods hinges upon factors such as design complexity and production volume—both crucial elements influencing cost-effectiveness in any project involving plastics like those seen with injection molding vs extrusion discussions.
Material Considerations

When diving into the world of manufacturing processes, material choice is paramount, especially in the debate of injection molding vs extrusion. Both methods utilize different grades of plastics tailored to their specific requirements, which can significantly influence product quality and performance. Understanding these differences helps manufacturers make informed decisions about their production needs.
Injection Grade vs Extrusion Grade Plastics
The distinction between injection grade and extrusion grade plastics is crucial for manufacturers deciding between injection molding vs extrusion. Injection grade plastics are designed to flow easily under pressure, making them ideal for creating complex shapes with high precision. In contrast, extrusion grade plastics are formulated for continuous flow, allowing them to be shaped into long profiles but often at the expense of intricate details.
So, what is the difference between extrusion grade and injection grade? While both types serve their purpose effectively within their respective processes, injection molding typically requires materials that can withstand higher temperatures and pressures during production. This results in stronger parts that can handle demanding applications compared to some extruded products.
Best Materials for Injection Molding
When it comes to selecting materials for injection molding, a variety of options are available that cater to different needs and applications. Common choices include acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), polycarbonate (PC), and polypropylene (PP), each offering unique advantages such as impact resistance or thermal stability. These materials not only meet the rigorous demands of injection molding but also provide excellent surface finishes and design flexibility.
However, one must consider the disadvantages of injection molding as well; while it may produce high-quality parts quickly once set up, initial tooling costs can be steep compared to other methods like extrusion moulding. Therefore, weighing the benefits against potential drawbacks is essential when determining if this method suits your project best.
Optimal Choices for Extrusion Moulding
Extrusion moulding thrives on a different set of material characteristics due to its continuous processing nature. Thermoplastics such as polyethylene (PE) and polystyrene (PS) are often favored because they exhibit excellent flow properties during the extrusion process while remaining cost-effective. These materials allow manufacturers to create long lengths with uniform cross-sections efficiently.
Is extrusion better than injection molding? It depends on your specific application needs! For projects requiring long continuous shapes or profiles—like pipes or sheets—extrusion shines through its efficiency and lower operational costs compared to traditional injection methods. Ultimately, understanding your material options is key in navigating the complexities of both processes in order to optimize production outcomes.
Design Flexibility
Complex Shapes with Injection Molding
Injection molding shines in its ability to create intricate shapes that would be challenging, if not impossible, with other methods. This process allows for detailed designs with undercuts, thin walls, and complex geometries, making it ideal for products like consumer electronics housings or automotive components. The precision achieved through injection molding often leads to superior aesthetics and functionality compared to extrusion processes.
However, one might wonder: is extrusion better than injection molding? While extrusion can produce long continuous shapes effectively, it struggles when tasked with complex forms. Thus, when weighing injection molding vs extrusion for detailed designs, injection molding typically takes the crown.
Extrusion’s Long Continuous Shapes
On the flip side of the coin is extrusion’s strength in producing long continuous shapes—think pipes, tubing, or even sheets of plastic material. This process excels at creating uniform profiles over extended lengths without interruptions or seams. The efficiency of extrusion means that manufacturers can quickly produce large volumes of consistent products.
That said, while extrusion offers remarkable efficiency for specific applications—like those requiring consistent cross-sections—it lacks the versatility needed for more complicated designs found in injection molding projects. Therefore, if your project demands long runs of simple shapes without much variation or detail, then extrusion moulding might be your best bet.
Limitations of Each Method
Despite their respective advantages, both injection molding and extrusion come with their own set of limitations that should be considered during production planning. For instance, while injection molding allows for highly detailed designs and a variety of materials like injection grade plastics tailored to specific applications, it does have higher initial setup costs and longer lead times due to mold creation processes.
Conversely, while extrusion provides cost-effective solutions for producing long continuous items at scale—often utilizing lower-cost materials like those suitable for extrusion grade—it may fall short on design intricacies and flexibility compared to its counterpart. Ultimately when evaluating injection molding vs extrusion cost-effectiveness alongside design needs; understanding these limitations is key to making an informed choice.
Production Efficiency
Speed Comparisons in Injection Molding
Injection molding is often celebrated for its rapid cycle times, allowing manufacturers to produce complex parts quickly and efficiently. In many cases, a single cycle can take anywhere from 15 seconds to a few minutes, depending on the part size and complexity. This speed makes injection molding particularly appealing for high-volume production runs, where time is money—hence the question: Is extrusion better than injection molding for quick turnaround projects?
Time Efficiency in Extrusion
On the other hand, extrusion is designed for continuous production, which means it can operate non-stop once set up properly. While individual extruded products may take longer to create compared to an injection-molded piece, the process itself allows for a steady output without interruption. Thus, when considering injection molding vs extrusion regarding time efficiency, it's essential to factor in that extrusion excels in producing large quantities of uniform shapes over extended periods.
Batch vs Continuous Production
The choice between batch and continuous production methods can significantly impact overall efficiency. Injection molding typically operates on a batch basis; each mold must be filled and cooled before another cycle begins—this can lead to downtime between batches.
Quality and Tolerance

Reliability of Injection Molding
Injection molding is renowned for its ability to produce high-quality parts with precise tolerances. This reliability stems from its capability to create complex shapes with intricate details that are difficult to achieve through other methods like extrusion. However, it's essential to consider that while injection molding excels in producing consistent parts, it does come with some disadvantages, such as longer setup times and higher initial costs compared to extrusion.
In terms of material quality, injection molding often uses specialized plastics designed for specific applications—these are known as injection grade materials. This focus on tailored materials enhances performance but raises questions like What is the difference between extrusion grade and injection grade? Ultimately, if you're looking for precision and detail in your plastic components, injection molding might just be your best bet.
Extrusion: Consistency Over Length
Extrusion stands out when it comes to producing long continuous shapes with uniformity throughout their length. This process allows manufacturers to create items like pipes or sheets that maintain consistent dimensions over extended distances—a feat that's hard to match with injection molding techniques. The question Is extrusion better than injection molding? often arises here; while it may not produce intricate details as effectively as its counterpart, its efficiency in creating uniform products makes it a strong contender.
Moreover, the consistency achieved through extrusion can significantly reduce production waste compared to batch processes like those used in injection molding. This advantage is particularly relevant when considering factors such as Injection molding vs extrusion vs plastic applications where uniformity plays a critical role in performance and usability across various industries.
Quality Control Measures in Both Methods
Both injection molding and extrusion rely on rigorous quality control measures to ensure final products meet industry standards. In injection molding processes, techniques such as statistical process control (SPC) monitor variables throughout production cycles—allowing manufacturers to catch defects early before they become costly issues down the line. On the flip side, extrusion also employs various monitoring systems that track dimensions continuously during production runs.
Quality assurance isn't just a checkbox; it's fundamental for maintaining competitiveness in markets driven by cost-effectiveness—hence why an analysis of injection molding vs extrusion cost must also include considerations about quality outcomes over time. By understanding how each method approaches quality control measures differently, businesses can make more informed decisions about which process aligns best with their operational needs.
Cost Analysis
Injection Molding vs Extrusion Cost Breakdown
In an injection molding vs extrusion cost breakdown, one must consider several factors that contribute to overall expenses. For instance, while injection molding often boasts a higher upfront investment due to mold creation and machinery setup, it can yield lower per-unit costs at high production volumes. Conversely, extrusion might be cheaper initially but could incur higher operational costs if not managed properly over time.
Initial Setup Costs vs Production Volume
Initial setup costs in injection molding are typically steep because of mold fabrication; however, these costs become less significant as production volume increases. Is extrusion better than injection molding when it comes to smaller runs? Not necessarily; although extrusion has a more affordable entry point for low-volume projects, its efficiency tends to shine when producing larger quantities consistently.
Long-term Savings in Each Method
Long-term savings in each method vary greatly depending on production needs and material usage. Injection molding may have higher initial expenses but offers substantial savings through reduced waste and faster cycle times at scale—perfect for high-demand items like consumer products or automotive parts. In contrast, while extrusion moulding is cost-effective for continuous products like pipes or sheets, its potential waste and slower speeds could offset those savings over time.
Environmental Impact
Sustainability in Injection Molding
Injection molding has made strides toward sustainability, particularly through advancements in material technology and recycling practices. Many manufacturers are now using biodegradable plastics or recycled materials in their injection molding processes, reducing reliance on virgin resources. However, one must consider that while injection molding can be efficient, its setup costs can be high; thus, weighing injection molding vs extrusion in terms of sustainability often depends on specific project requirements.
Extrusion and Its Plastic Waste Concerns
Extrusion moulding offers continuous production capabilities but is not without its drawbacks—plastic waste being a significant concern. During the extrusion process, any miscalculations or defects can lead to excess material that often ends up as scrap or waste. This raises an important question: Is extrusion better than injection molding when considering environmental impact? The answer may depend on how well each method manages waste and incorporates recycling initiatives.
Comparing Energy Consumption
Energy consumption is another critical factor when analyzing injection molding vs extrusion. Generally speaking, injection molding tends to consume more energy per cycle due to its complex machinery and heating requirements for melting plastics rapidly. In contrast, extrusion typically operates continuously over longer periods with lower energy peaks but may require significant power for sustained operations over time—highlighting that each method has its own energy profile depending on production needs.
Conclusion

In the battle of injection molding vs extrusion, both methods offer unique advantages and disadvantages that cater to different manufacturing needs. While injection molding excels in producing complex parts with high precision, extrusion shines in creating long continuous shapes efficiently. Understanding these key differences is essential for manufacturers looking to optimize their production processes.
Summarizing Key Differences
When comparing injection molding and extrusion, the most apparent distinction lies in their operational mechanics and output types. Injection molding is ideal for intricate designs requiring tight tolerances, while extrusion focuses on uniform profiles and continuous lengths. Additionally, the choice between extrusion grade and injection grade materials can significantly impact product performance; each has its specific applications that must be considered carefully.
Making the Choice: Injection Molding or Extrusion
Deciding whether extrusion is better than injection molding ultimately depends on your project requirements. If your products demand complex geometries or high-volume production runs, injection molding may be your best bet despite its higher initial setup costs. Conversely, if you need long sections of material with consistent quality over time, then extrusion moulding could be the more economical solution in terms of ongoing production costs.
Insights from the Baoyuan Team
The Baoyuan Team emphasizes a thorough analysis of both methods when contemplating your manufacturing strategy—consider factors like cost, efficiency, and material compatibility before making a final decision between injection molding vs extrusion. They also highlight that while there are disadvantages to each method—such as the longer lead times associated with setting up injection molds—understanding these trade-offs can lead to smarter choices that enhance productivity and reduce waste in the long run. Ultimately, it's about finding the right balance between quality and cost-effectiveness tailored to your specific needs.

