Introduction

Understanding Polycarbonate Injection Molding
Polycarbonate injection molding is a manufacturing technique that utilizes high temperatures to melt polycarbonate resin and inject it into molds to create precise shapes and components. The versatility of this material makes it a popular choice across numerous industries, from eyewear to automotive parts. But is polycarbonate good for injection molding? Absolutely! Its unique properties allow for intricate designs while maintaining strength and durability.
Comparing Plastic and Polycarbonate Lenses
The comparison between acrylic (plastic) lens vs polycarbonate lens often leads consumers to weigh their options carefully. While both materials have their merits, it's crucial to understand their differences in terms of performance and application suitability. For instance, one common question that arises is: what is a disadvantage of polycarbonate lenses? Although they are impact-resistant, they can be prone to scratching without proper coatings.
The Importance of Material Selection
Choosing the right material for your project can significantly affect both functionality and cost-efficiency in production processes like injection molding. Questions such as What is the best material for plastic injection molding? often emerge during this selection phase, highlighting the need for informed decisions based on specific requirements. Additionally, having access to a comprehensive polycarbonate injection molding processing guide can streamline this decision-making process by providing valuable insights into temperature guidelines and other critical factors.
What is Polycarbonate?
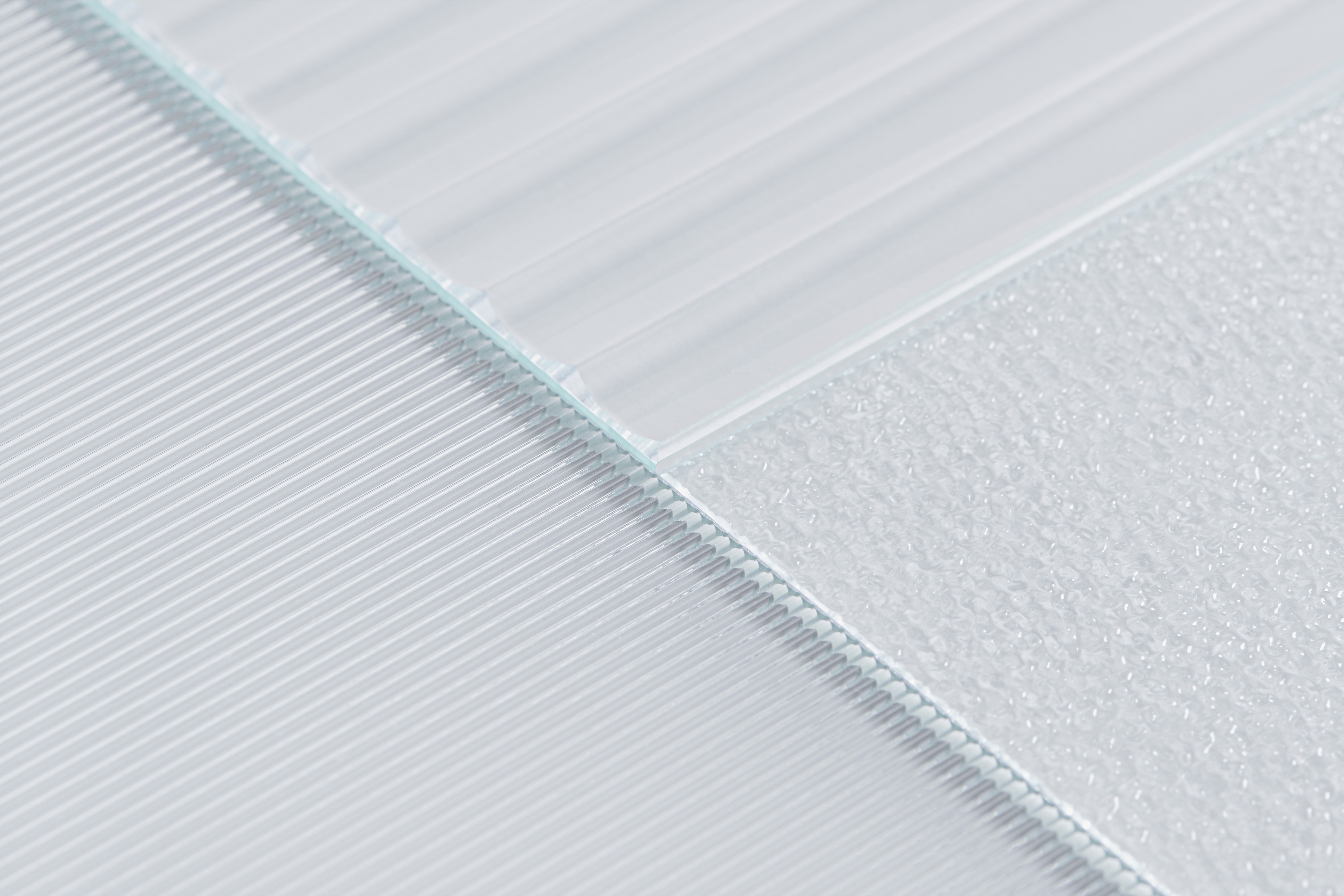
Polycarbonate is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional strength and versatility. Often used in various applications, it stands out in the world of materials due to its unique properties that make it suitable for both everyday items and specialized products. Understanding polycarbonate is essential, especially when comparing options like plastic vs. polycarbonate lenses.
Properties of Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate boasts impressive properties that make it a favorite among manufacturers. It is highly impact-resistant, which means it can withstand significant force without breaking—a crucial factor when considering which is better, plastic or polycarbonate lenses? Additionally, polycarbonate has excellent clarity and optical performance, making it an ideal choice for applications requiring transparency and durability.
Another notable property of polycarbonate is its temperature resistance; this makes it suitable for a variety of environments without compromising its integrity. However, while discussing the advantages, one must also consider what is a disadvantage of polycarbonate lenses—such as their susceptibility to scratching compared to other materials like acrylic. Overall, the combination of strength and clarity positions polycarbonate as a top contender in material selection.
Why Choose Polycarbonate?
Choosing polycarbonate over other materials can be a game-changer for many projects. Its lightweight nature makes it easier to handle and install than heavier alternatives while still providing superior durability—this often leads to questions about whether polycarbonate is good for injection molding or not. Moreover, the versatility in design allows for innovative shapes and structures that are difficult to achieve with traditional plastics.
Polycarbonate also excels in safety features; it's often used in eyewear lenses due to its shatterproof quality—this makes it particularly appealing when weighing plastic vs. polycarbonate lens options for protective gear or eyewear products. Additionally, with advancements in technology, manufacturers have developed coatings that enhance UV resistance and scratch resistance—addressing some common concerns regarding disadvantages of polycarbonate lenses.
Applications of Polycarbonate
The applications of polycarbonate are vast and varied across numerous industries. From automotive components to electronic housings and medical devices, this material's adaptability shines through—making it an excellent choice when determining what is the best material for plastic injection molding projects. In optics, both acrylic lens vs polystyrene lens comparisons highlight how polycarbonates offer superior performance under stress while maintaining visual clarity.
In construction and architecture, transparent roofing panels made from polycarbonates provide natural light without compromising safety or insulation properties—a perfect example of their multifunctionality! As we delve deeper into specific uses within industries like consumer electronics or safety equipment, the benefits become even more pronounced through practical applications tailored using techniques such as the detailed “polycarbonate injection molding processing guide.”
The Polycarbonate Injection Molding Process
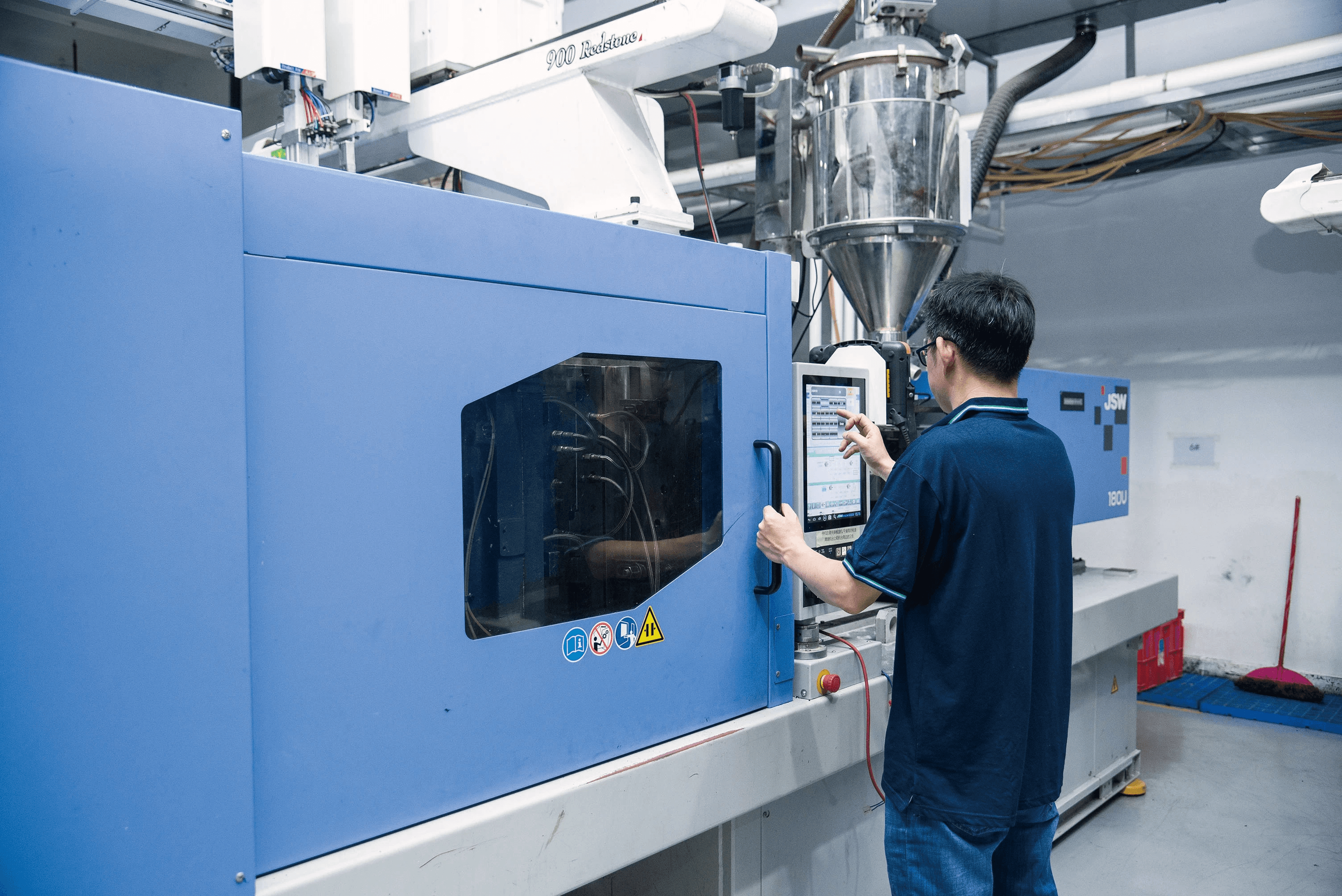
Polycarbonate injection molding is a fascinating process that transforms raw polycarbonate material into intricate shapes and designs. This method is particularly popular for creating lenses, components in electronics, and various consumer products due to polycarbonate's unique properties. Understanding the steps involved, the necessary equipment, and temperature guidelines can help you navigate this process effectively.
Steps in Injection Molding
The injection molding process begins with the preparation of polycarbonate pellets, which are heated until they melt into a viscous liquid. This molten material is then injected into a mold under high pressure, allowing it to fill every nook and cranny of the mold's design. Once cooled, the mold is opened to reveal the finished product—often with minimal post-processing required due to polycarbonate’s excellent flow characteristics.
In comparing plastic vs. polycarbonate lens production specifically, it's clear that each step in injection molding must be meticulously executed to ensure quality outcomes. For example, if you're pondering Which is better, plastic or polycarbonate lenses? consider how precise molds can lead to superior lens clarity and performance when using polycarbonate materials. Thus, understanding these steps not only enhances production efficiency but also informs decisions on material selection.
Equipment Used in Injection Molding
The heart of any injection molding operation lies in its equipment: from injection molding machines to auxiliary tools like dryers and chillers. An injection molding machine consists of a hopper for feeding raw material, a barrel for heating and mixing it, and an injector that forces the molten material into molds at high pressure. For those considering whether Is polycarbonate good for injection molding?, you'll find that its compatibility with standard equipment makes it an ideal choice for many manufacturers.
Additionally, specialized molds designed for specific applications can greatly enhance productivity when working with polycarbonate materials compared to alternatives like acrylic lens vs polycarbonate lens options. The right machinery not only ensures precision but also reduces waste during production—a critical factor when evaluating What is the best material for plastic injection molding? Ultimately, investing in quality equipment pays off in both efficiency and product quality.
Polycarbonate Injection Molding Temperature Guidelines
Temperature control during the injection molding process plays a vital role in determining final product quality—especially when working with materials like polycarbonate known for their thermal sensitivity. Typically, processing temperatures range between 550°F (288°C) and 650°F (343°C), ensuring optimal flow while avoiding degradation of the polymer structure. If you're concerned about What is a disadvantage of polycarbonate lenses?, remember that improper temperature management can lead to issues such as warping or discoloration.
Following a well-structured **polycarbonate injection molding processing guide** helps maintain these critical temperature parameters throughout production runs while minimizing defects associated with overheating or underheating materials. When comparing acrylic lens vs polycarbonate lens manufacturing processes further down this guide—understanding these nuances will provide insight into why many manufacturers choose polycarbonates despite their drawbacks such as UV resistance challenges or scratching concerns.
Advantages of Polycarbonate Over Other Materials

Strength and Durability
One of the most compelling reasons to choose polycarbonate is its exceptional strength and durability. Unlike standard plastic lenses that can crack or shatter under impact, polycarbonate lenses are robust enough to withstand significant stress without damage. This makes them an ideal choice for safety glasses or protective eyewear, where the question of Which is better, plastic or polycarbonate lenses? often leans heavily towards polycarbonate due to its superior resilience.
Moreover, when evaluating Is polycarbonate good for injection molding?, the answer is a resounding yes! Its ability to maintain structural integrity under various conditions means it performs exceptionally well in the injection molding process. This strength not only ensures longevity but also reduces replacement costs over time—a win-win situation for manufacturers and consumers alike.
Lightweight Compared to Alternatives
When it comes to weight, polycarbonate shines brighter than many other materials on the market. While traditional glass lenses can be cumbersome and heavy, polycarbonate offers a lightweight alternative that doesn’t compromise on quality or performance. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in applications such as eyewear; users often find themselves asking about plastic vs.polycarbonate lens options because they appreciate how much lighter and more comfortable polycarbonate feels.
Furthermore, this lightweight nature allows designers greater freedom when creating products without worrying about added bulkiness affecting usability or aesthetics. For those contemplating What is the best material for plastic injection molding?, consider how much easier handling lighter components can make assembly processes—less strain on workers means increased efficiency!
Versatility in Design
Polycarbonate's versatility extends far beyond just being strong and lightweight; it also offers incredible design flexibility that few materials can match. Whether you're looking at an acrylic lens vs polycarbonate lens comparison or considering intricate shapes and sizes for your project, polycarbonate adapts seamlessly to various molds during the injection molding process. This adaptability opens up a world of possibilities for designers who want their products not only functional but also visually appealing.
Additionally, with its excellent optical clarity and ability to be tinted or treated with coatings (like anti-scratch finishes), polycarbonate allows manufacturers to create customized solutions tailored specifically to their customers' needs—making it a top contender in both industrial applications and consumer products alike! For those interested in diving deeper into production specifics, a thorough review of the polycarbonate injection molding processing guide will reveal even more about how this remarkable material can elevate your designs.
Common Disadvantages of Polycarbonate

While polycarbonate lenses are often hailed for their strength and versatility, they aren't without their drawbacks. Understanding these disadvantages is crucial when deciding between plastic vs. polycarbonate lenses, especially if you're weighing the options for eyewear or other applications. Let's dive into some of the key disadvantages associated with polycarbonate lenses.
What is a Disadvantage of Polycarbonate Lenses?
One significant disadvantage of polycarbonate lenses is their susceptibility to scratching. Unlike glass, which can be highly scratch-resistant, polycarbonate requires additional coatings to enhance its durability against everyday wear and tear. This raises the question: which is better, plastic or polycarbonate lenses? While both materials have pros and cons, the need for protective coatings may make some users lean toward traditional plastic options.
UV Resistance Challenges
Polycarbonate does offer inherent UV protection; however, it can struggle with long-term exposure to sunlight. Over time, prolonged UV exposure may lead to yellowing or degradation of the lens material itself. Therefore, while it’s tempting to label polycarbonate as superior due to its initial UV resistance, understanding these challenges can help you make informed decisions about whether it's suitable for your needs—especially when comparing acrylic lens vs polycarbonate lens options.
Scratching and Surface Degradation
Scratching isn't just a minor inconvenience; it can significantly affect visibility over time and detract from the aesthetic appeal of your lenses. Even with hard coatings applied during manufacturing processes like injection molding—where knowing how to navigate the polycarbonate injection molding processing guide becomes essential—scratches can still occur under certain conditions. This underscores why considering what is a disadvantage of polycarbonate lenses is vital in determining if they are indeed the best material for plastic injection molding in your specific application.
Comparing Acrylic and Polycarbonate Lenses

When it comes to choosing the right lens material, the debate often boils down to acrylic lens vs polycarbonate lens. Both materials have their own unique properties and applications, but polycarbonate lenses tend to edge out in terms of performance and durability. While acrylic is known for its clarity and low cost, polycarbonate offers enhanced strength, making it more suitable for safety glasses and high-impact environments.
Acrylic Lens vs Polycarbonate Lens
Acrylic lenses are lightweight and provide excellent optical clarity, making them a popular choice for various applications. However, when comparing plastic vs polycarbonate lens options, the latter shines due to its superior impact resistance. In fact, polycarbonate lenses are nearly 10 times more impact-resistant than acrylic lenses, which is a significant advantage in safety-critical situations.
Polycarbonate also has built-in UV protection that makes it an excellent choice for outdoor activities or eyewear. While both materials can be scratched easily, polycarbonate's resilience means it's better suited for everyday wear in demanding conditions. Ultimately, understanding these differences can help you decide which material aligns best with your needs.
Which is Better, Plastic or Polycarbonate Lenses?
The question Which is better, plastic or polycarbonate lenses? often arises among consumers looking for the best value for their money. Plastic lenses generally refer to traditional CR-39 lenses that are lighter but lack the robustness of polycarbonate options. If you're considering durability alongside weight considerations, polycarbonate emerges as a clear winner due to its strength and lightweight nature.
Moreover, if you’re planning on using your lenses in environments where they might be subjected to impact or stress (think sports or industrial settings), the advantages of polycarbonate become even more pronounced. However, if budget constraints are a primary concern and you don’t require high-impact resistance or UV protection, traditional plastic may still serve your needs adequately.
Cost Considerations
Cost plays an essential role in determining whether acrylic or polycarbonate is right for you—especially when weighing factors like Is polycarbonate good for injection molding? The truth is that while initial costs may be higher for polycarbonate materials compared to standard plastics like CR-39 acrylics, the long-term benefits typically justify this investment due to their longevity and reduced need for replacements.
When considering cost-effectiveness in relation to performance metrics such as durability and UV resistance—it's essential to assess what you value most in your lens choice. For projects requiring high-quality output with minimal maintenance over time—polycarbonate proves itself as one of the best materials for plastic injection molding despite its higher upfront price tag.
Conclusion

In wrapping up our exploration of polycarbonate injection molding, it’s clear that this material plays a pivotal role in various applications, particularly when comparing plastic vs. polycarbonate lenses. Understanding the properties of polycarbonate and the nuances of its injection molding process can help you make informed decisions for your projects. Whether you're considering strength, weight, or design versatility, polycarbonate stands out as a compelling choice.
Key Takeaways on Polycarbonate Injection Molding
Polycarbonate is an exceptional material for injection molding due to its durability and lightweight nature, making it ideal for products requiring resilience without added bulk. However, one must consider the disadvantages of polycarbonate lenses, such as their susceptibility to scratching and UV resistance challenges. Ultimately, mastering the polycarbonate injection molding temperature guidelines is crucial for achieving optimal results in production.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
When deciding between plastic vs. polycarbonate lenses, it's essential to weigh factors like application requirements and cost implications carefully. While some may wonder which is better—plastic or polycarbonate lenses—the answer often lies in specific use cases; polycarbonate tends to excel in high-impact environments but may not be the most cost-effective option for every application. Evaluating whether polycarbonate is good for injection molding will depend on your project's unique demands and specifications.
Insights from the Baoyuan Team on Injection Molding
The Baoyuan team's expertise highlights that understanding what is the best material for plastic injection molding involves more than just looking at price tags; it's about performance under stress and longevity over time. They emphasize that a solid grasp of acrylic lens vs polycarbonate lens comparisons can guide manufacturers toward making choices that align with consumer needs while also adhering to budget constraints. Lastly, they recommend consulting a thorough Polycarbonate injection molding processing guide to navigate complexities effectively.

