Introduction
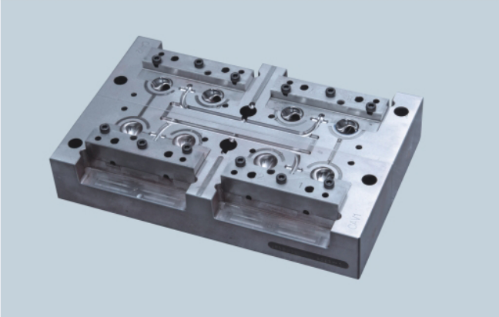
Welcome to the fascinating world of plastic molding, where raw materials transform into the products we use every day! If you've ever wondered how is plastic molded into everything from containers to car parts, you're in the right place. This introduction will guide you through the importance of plastic molding in manufacturing and give you a peek into various molding methods that make it all possible.
Understanding Plastic Molding Techniques
Plastic molding techniques are essential processes that shape plastics into usable forms. The question What is plastic injection molding? often arises, as this technique stands out among the various methods available. In fact, understanding these techniques can help manufacturers choose the best approach for their specific needs and applications.
Importance of Plastic Molding in Manufacturing
Plastic molding plays a pivotal role in modern manufacturing by enabling mass production with precision and efficiency. The ability to create complex shapes at scale is crucial for industries ranging from automotive to consumer goods. With its versatility, plastic molding not only reduces production costs but also enhances product quality, making it an indispensable element of contemporary manufacturing.
Overview of Various Molding Methods
There are five primary types of plastic moulding: injection moulding, blow moulding, compression moulding, rotational moulding, and thermoforming. Each method has unique characteristics that suit different applications and material types. By exploring these five types of plastic moulding, manufacturers can identify which process aligns best with their design requirements and production goals.
Injection Molding
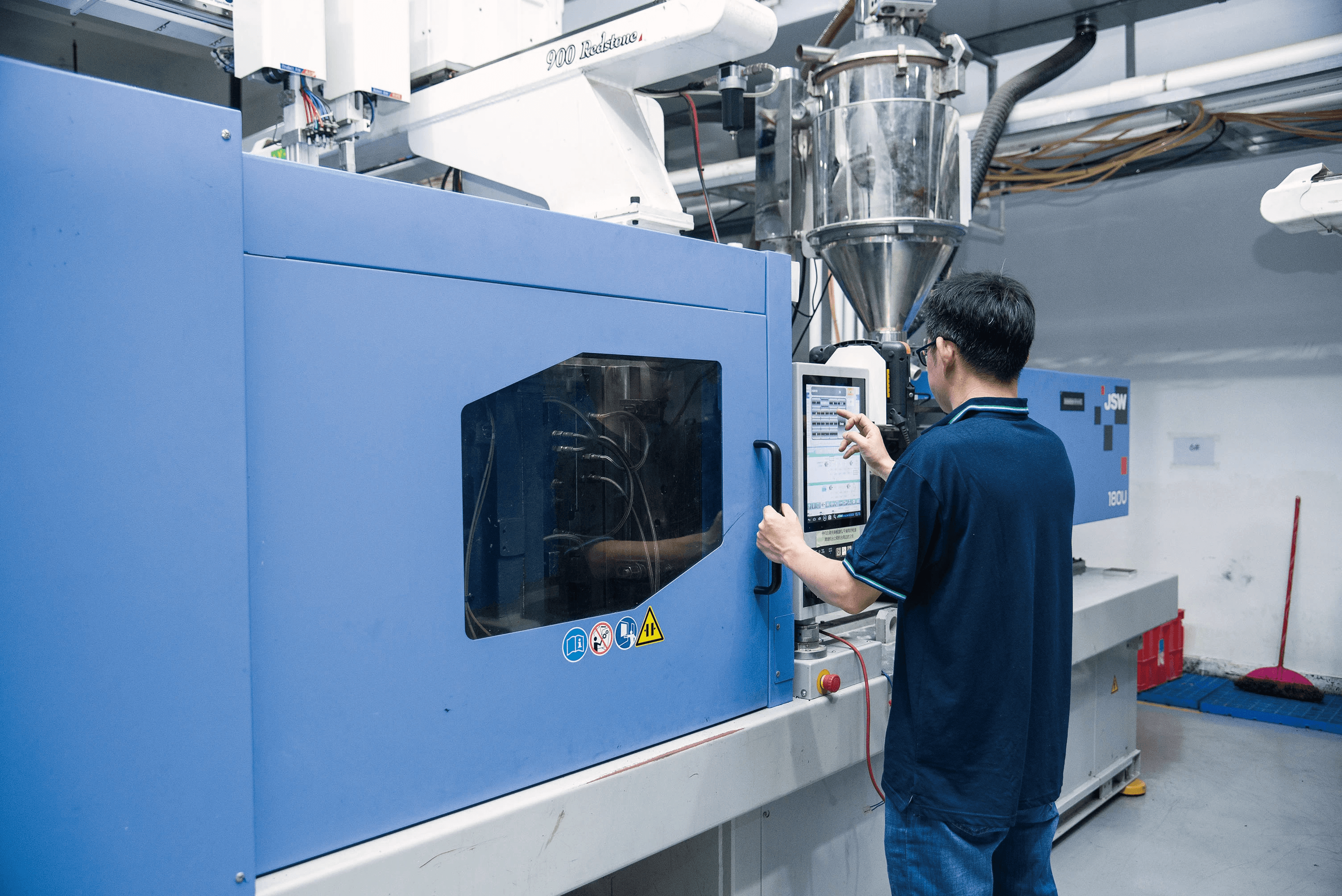
Injection molding stands as one of the most widely used manufacturing processes for creating plastic parts. But how is plastic molded? The process involves heating plastic until it becomes a viscous liquid, which is then injected into a mold under high pressure. Once cooled, the mold opens to reveal the finished product, making it a highly efficient method for mass production.
How Injection Molding Works
So, what is plastic injection molding? It begins with raw plastic pellets that are heated in a barrel until they melt into a thick liquid. This molten plastic is then forced into a precisely designed mold cavity using an injection unit, where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape. The entire process can be automated for speed and consistency, making it ideal for producing large quantities of identical parts quickly.
Advantages of Injection Molding
One of the primary advantages of injection molding is its ability to produce complex shapes with high precision and repeatability. Additionally, this method allows for minimal waste since excess material can often be recycled back into the process. Other benefits include faster production cycles and reduced labor costs compared to other techniques—making it one of the top choices among manufacturers when considering the 5 types of plastic moulding.
Key Applications of Injection Molding
Injection molding finds applications across various industries due to its versatility and efficiency. From automotive components to consumer goods like toys and kitchenware, nearly every sector utilizes this technique in some form or another. Its ability to create intricate designs while maintaining structural integrity makes it an essential tool in modern manufacturing practices.
The Role of Baoyuan in Injection Molding Solutions
Baoyuan has established itself as a leader in providing innovative injection molding solutions tailored to meet diverse industry needs. With advanced technology and expertise, Baoyuan helps businesses optimize their manufacturing processes by offering customized molds that enhance quality and reduce cycle times. By partnering with Baoyuan, companies can leverage cutting-edge techniques to improve their products while embracing sustainable practices in line with future trends.
Blow Molding
Blow molding is a fascinating plastic molding technique that allows manufacturers to create hollow plastic parts efficiently. This method is particularly effective for producing containers, bottles, and other hollow shapes that require uniform thickness and strength. In this section, we will delve into the blow molding process, its benefits, and the various industries that rely on this innovative technique.
The Blow Molding Process Explained
So, how is plastic molded using blow molding? The process begins with melting plastic resin and forming it into a parison—a tube-like piece of molten plastic. This parison is then clamped between two mold halves and air is blown into it, expanding the plastic to fit the mold’s shape. As the air fills the parison, it takes on the form of the mold cavity, creating a hollow object.
Once cooled and solidified, the newly formed item can be removed from the mold. This method allows for rapid production rates and can handle large volumes of product with minimal waste. Overall, blow molding stands out among various methods like injection moulding due to its efficiency in creating lightweight yet durable products.
Benefits of Blow Molding
The benefits of blow molding are numerous and make it an attractive option for manufacturers looking for cost-effective solutions. For starters, this method offers high production speeds which translate to lower costs per unit—ideal for mass production runs. Additionally, blow-molded products often feature seamless designs that enhance their structural integrity while minimizing material usage.
Another significant advantage lies in versatility; blow molding can accommodate a wide range of materials including polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP). As a result, manufacturers can produce everything from simple bottles to complex industrial containers with ease. With these benefits in mind, it's clear why many companies prefer blow molding over other techniques when considering what is plastic injection molding or exploring 5 types of plastic moulding.
Industries Using Blow Molding
Blow molding finds applications across various industries due to its adaptability and efficiency in producing hollow shapes. One prominent industry includes beverage manufacturing where companies produce an array of bottles—from soda to water—that require consistent quality at scale. Additionally, consumer goods such as household cleaning products often utilize blow-molded containers for their lightweight yet sturdy characteristics.
The automotive sector also employs blow molding techniques for producing fuel tanks and other components that need both durability and precision engineering. Furthermore, packaging industries benefit significantly from this process by creating custom-shaped packaging solutions tailored to specific product needs—showcasing just how versatile blow molding truly is!
Compression Molding
Compression molding is a fascinating process that’s been around for quite some time, and it’s one of the five types of plastic molding that manufacturers often rely on. This method involves placing a pre-measured amount of plastic material into a heated mold cavity, where it is then compressed under pressure to take the shape of the mold. The heat and pressure work together to soften the plastic, allowing it to flow and fill the mold completely, resulting in a solid part once cooled.
What is Compression Molding?
So, what is compression molding? At its core, it's a technique used primarily for thermosetting plastics, where heat causes the material to harden permanently after being molded. Unlike injection molding—which is another popular method—compression molding doesn’t inject molten plastic; instead, it uses solid or semi-solid materials that are transformed into finished products through heat and pressure.
This method can be particularly effective for larger parts or products with complex geometries. It’s also worth noting that compression molding can accommodate different types of materials beyond just plastics, making it versatile in various manufacturing settings. When considering how plastic is molded using this technique, one must appreciate its efficiency and adaptability in producing high-quality components.
Pros and Cons of Compression Molding
Like any manufacturing process, compression molding comes with its own set of pros and cons that should be carefully weighed. One significant advantage is its ability to produce large parts quickly without requiring extensive tooling changes—ideal for high-volume production runs. Additionally, because it uses less energy compared to methods like injection moulding, manufacturers can enjoy cost savings while reducing their environmental footprint.
On the flip side, there are some drawbacks to consider as well. The initial setup costs can be higher due to the need for specialized molds that endure high pressures and temperatures over time. Furthermore, achieving precise tolerances can be more challenging than other methods like injection molding; thus requiring careful attention during production planning.
Typical Uses of Compression Molding
Compression molding finds applications across various industries thanks to its versatility in creating durable products from thermosetting plastics or rubber materials. Common examples include automotive parts such as bumpers or dashboards—where strength and resistance are paramount—and electrical components like insulators or connectors that require excellent thermal stability.
Additionally, this technique shines when producing household items such as kitchenware or bathroom fixtures where aesthetic appeal meets functionality. So whether you're curious about how plastic is molded into your favorite car part or wondering about what goes into your everyday kitchen gadgets, compression molding plays an integral role in delivering quality solutions across multiple sectors.
Rotational Molding
Rotational molding is a fascinating process that allows manufacturers to create hollow plastic parts with remarkable precision. Unlike other methods such as injection molding, where molten plastic is injected into a mold, rotational molding involves heating plastic powder in a mold that is rotated along two axes. This unique approach ensures an even distribution of material, resulting in strong and seamless products.
Understanding Rotational Molding
So, how is plastic molded using this technique? In rotational molding, the plastic powder is placed inside a hollow mold and then heated in an oven while being rotated. The heat causes the powder to melt and adhere to the walls of the mold, creating a uniform layer of plastic as it cools and solidifies. This method stands out among the 5 types of plastic moulding due to its ability to produce large parts without seams or weld lines.
One of the key advantages of rotational molding lies in its versatility; it can accommodate complex shapes and varying wall thicknesses with ease. Additionally, it allows for the incorporation of different materials or colors within the same product during production. As a result, understanding rotational molding opens up possibilities for innovative design solutions that other methods may struggle to achieve.
When to Choose Rotational Molding
Choosing rotational molding over other techniques like injection moulding often boils down to specific project requirements. If your project calls for large, hollow parts with consistent wall thickness—think tanks or playground equipment—rotational molding might be your best bet. It’s particularly advantageous when you need low-volume production runs since tooling costs are generally lower than those associated with injection moulding.
Moreover, if you’re working with materials that require gentle handling during processing or if your design includes intricate features, this method shines brightly in comparison to traditional methods like compression or blow molding. Rotational molding also allows for excellent surface finishes and can easily incorporate additional features such as inserts or reinforcements during production.
Product Examples of Rotational Molding
When we talk about what products are made through rotational molding, think big! Common examples include water tanks, kayaks, playground equipment, and even large storage containers—items that benefit from being lightweight yet durable thanks to this process's seamless construction. The flexibility offered by rotational molding makes it ideal for various industries including automotive (fuel tanks), agricultural (chemical containers), and recreational (toys).
Another notable example includes custom packaging solutions where shape and durability are critical factors; these items demonstrate how versatile this technique truly is compared to others like injection moulding or compression methods. With so many applications available through rotational molding techniques coupled with its unique advantages over other types listed among the 5 types of plastic moulding—it’s no wonder manufacturers are increasingly turning toward this method for their production needs.
Thermoforming
Thermoforming is a fascinating process that transforms flat plastic sheets into three-dimensional shapes. By heating the plastic until it becomes pliable, manufacturers can mold it over various forms to create products tailored to specific needs. This technique falls under the umbrella of the 5 types of plastic moulding, showcasing its versatility and effectiveness in modern manufacturing.
Exploring Thermoforming Techniques
In the realm of how is plastic molded, thermoforming stands out for its straightforward yet effective approach. The process typically involves heating a thermoplastic sheet until it softens and then forming it over a mold using vacuum pressure or mechanical force. This method allows for intricate designs and can accommodate large-scale production runs with relative ease, making it an appealing choice for many industries.
Thermoforming techniques can be categorized into two main types: vacuum forming and pressure forming. Vacuum forming uses atmospheric pressure to pull the heated sheet onto the mold, while pressure forming applies additional air pressure to achieve finer details and smoother finishes. Understanding these techniques is essential for manufacturers looking to optimize their production processes and product quality.
Benefits of Thermoforming
One of the standout benefits of thermoforming is its cost-effectiveness compared to other molding methods like injection moulding or compression molding. It requires less energy and fewer materials, which translates into lower production costs without sacrificing quality. Additionally, since thermoformed products often require minimal secondary operations, manufacturers can save both time and money in their production cycles.
Another advantage lies in the material flexibility; various thermoplastics can be used depending on desired properties such as strength, transparency, or resistance to chemicals. This adaptability makes thermoforming suitable for a wide range of applications across multiple industries—from packaging solutions to automotive parts—demonstrating its role as one of the key players among the 5 types of plastic moulding methods available today.
Moreover, thermoformed products are often lighter than those produced through other methods like injection moulding, making them ideal for applications where weight savings are crucial—think packaging materials or components in aerospace engineering! Ultimately, this technique not only streamlines manufacturing but also enhances product performance across diverse sectors.
Common Products Made by Thermoforming
When we delve into what is plastic injection molding versus thermoforming, it's essential to recognize that each method serves unique purposes within manufacturing realms. However, thermoforming excels at producing items like trays, containers, clamshells, and even large panels used in construction or transportation industries—showcasing its versatility in creating both simple and complex shapes efficiently.
Some common examples include food packaging containers that benefit from being lightweight yet sturdy enough for transport; medical trays designed with precision that ensure safety during usage; and custom signage that requires durability without excessive weight—demonstrating how this technique meets varied market demands effectively.
In conclusion, understanding how is plastic molded through techniques like thermoforming opens up numerous possibilities for innovation within manufacturing processes while addressing practical needs across different sectors effectively.
Conclusion
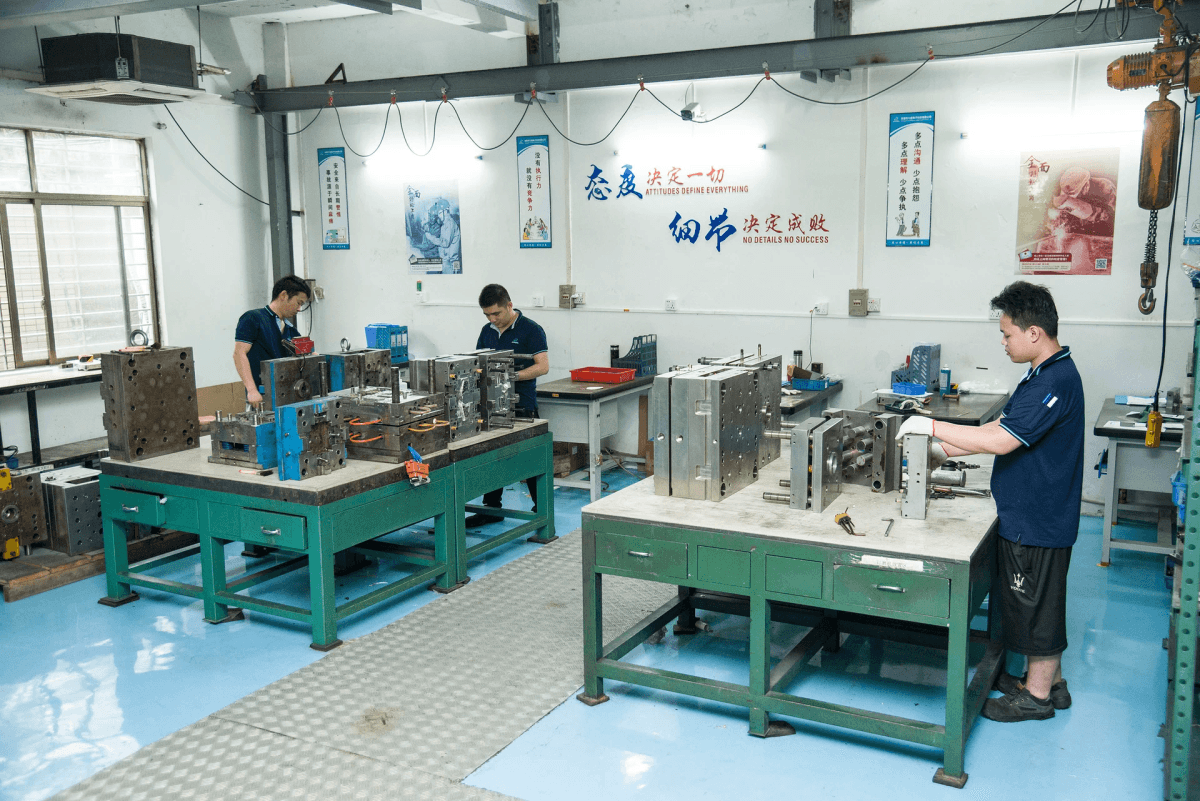
In the realm of manufacturing, understanding how plastic is molded is crucial for selecting the right technique for your project. With multiple molding methods available, each offering unique benefits and applications, companies must carefully assess their needs to make informed decisions. From injection molding to rotational molding, the right choice can significantly impact production efficiency and product quality.
Choosing the Right Molding Method
When it comes to choosing among the 5 types of plastic moulding, factors such as production volume, material type, and desired product characteristics come into play. For instance, if you’re looking for high precision and complex shapes, injection moulding might be your best bet. However, if you're working with larger items or lower volumes, techniques like blow molding or rotational molding could be more suitable options.
Understanding what is plastic injection molding and how it differs from other methods is essential in this decision-making process. Each technique has its own set of pros and cons that can affect everything from costs to lead times. Ultimately, a thorough evaluation will ensure that you select a method that aligns with your project goals while optimizing resources.
The Role of Baoyuan in Injection Molding Solutions
Baoyuan stands out in the world of injection molding solutions by providing tailored services that meet diverse client needs. Their expertise in injection moulding allows them to deliver high-quality products efficiently while ensuring cost-effectiveness for various industries. With a commitment to innovation and customer satisfaction, Baoyuan plays a pivotal role in helping businesses navigate the complexities of what is plastic injection molding.
As companies increasingly turn to Baoyuan for their injection molding needs, they benefit from advanced technology and skilled craftsmanship that enhance product performance. Whether it's developing prototypes or scaling up production runs, Baoyuan's solutions are designed to streamline processes while maintaining exceptional quality standards. This partnership not only boosts productivity but also fosters long-term growth in an ever-evolving market.
Future Trends in Plastic Molding Technology
Looking ahead at future trends in plastic molding technology reveals exciting advancements on the horizon that promise to revolutionize manufacturing processes further. Innovations such as 3D printing integration with traditional methods like injection moulding are gaining traction—offering unprecedented design flexibility while reducing waste materials significantly. Additionally, sustainable practices are becoming more prevalent as manufacturers explore biodegradable plastics and energy-efficient machinery.
As we delve deeper into these trends, understanding how plastic is molded will become increasingly important for industry professionals seeking to stay competitive. By embracing cutting-edge technologies alongside traditional techniques like compression or thermoforming, manufacturers can adapt swiftly to changing consumer demands while minimizing environmental impact. The future holds immense potential for those willing to innovate within this dynamic field.

