Introduction
In the world of manufacturing, two prominent processes stand out for their efficiency and versatility: blow molding and injection molding. Understanding the nuances between these methods is crucial for anyone looking to optimize production or innovate designs in their products. This introduction will explore the fundamental differences, key applications, and the critical role material selection plays in determining which process to use.
Understanding Blow Molding and Injection Molding
Blow molding vs injection molding often sparks debates among manufacturers, as each technique has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Blow molding is primarily used for creating hollow plastic parts, while injection molding excels at producing solid components with intricate details. The three types of blow molding—extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding, and stretch blow molding—each serve specific purposes that cater to different product requirements.
Key Applications for Each Process
Blow molding is commonly employed in the production of bottles, containers, and other hollow items due to its ability to create lightweight yet durable products efficiently. In contrast, injection molding shines in applications requiring precision and complexity, such as automotive parts or consumer electronics casings. Understanding what blow molding is used for versus the capabilities of injection molding can help businesses make informed decisions about which method aligns best with their project goals.
The Importance of Material Selection
Material selection plays a pivotal role when comparing blow molding vs injection molding processes; it can significantly impact both performance and cost-effectiveness. Choosing the right materials ensures that products meet necessary standards while optimizing production efficiency. Factors such as durability, flexibility, and cost must be considered when selecting materials for either process to achieve desired outcomes without compromising quality.
What is Blow Molding?
Blow molding is a manufacturing process used to create hollow plastic parts by inflating heated plastic inside a mold. This technique is particularly popular for producing bottles, containers, and various other items where a hollow shape is advantageous. Understanding blow molding requires an exploration of its intricate processes, types, and materials.
The Process Explained
The blow molding process begins with the heating of thermoplastic material until it reaches a pliable state. Once softened, the material is formed into a parison—a tube-like structure that will be inflated into the desired shape. Air is then blown into the parison while it’s inside a mold, causing it to expand and take on the mold's shape, creating a finished product that can be cooled and ejected.
In terms of efficiency, blow molding stands out against injection molding due to its ability to produce lightweight yet durable products in high volumes. However, potential drawbacks include limitations in design complexity compared to injection molding; this leads many manufacturers to weigh their options carefully when considering blow molding vs injection molding for their projects. Ultimately, understanding what blow molding is and how it works can help businesses make informed decisions about their production needs.
Types of Blow Molding Techniques
There are three primary types of blow molding techniques: extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding, and stretch blow molding. Extrusion blow molding involves extruding molten plastic into a parison form before blowing it up in the mold—this method is widely used for making large containers like barrels or tanks. Injection blow molding combines elements from both processes: plastic is first injected into a preform shape before being blown into its final form; this technique allows for greater precision in smaller products such as cosmetic bottles.
Stretch blow molding takes advantage of stretching the preform during inflation to enhance strength and clarity—this method is commonly used for producing PET bottles due to its superior properties. Each technique comes with unique advantages that cater to specific applications; thus understanding these differences can help manufacturers choose wisely between them when evaluating options like extrusion vs injection methods or assessing what are the three types of blow Moulding available.
Common Materials Used in Blow Molding
When discussing materials suitable for blow molding, polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) lead the pack due to their excellent properties such as flexibility and resistance to impact. Other materials like polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are also utilized but come with certain limitations regarding temperature resistance compared to PE or PP—these factors play crucial roles in determining which material best fits specific applications within the realm of what is blow molding used for.
Additionally, companies need to consider how material selection impacts production costs; typically, using lower-cost materials may lead some businesses down an attractive path when evaluating blow molding vs injection molding cost implications. However, it's essential not only to focus on costs but also on performance characteristics as subpar material choices could result in higher long-term expenses related to durability issues or product failures.
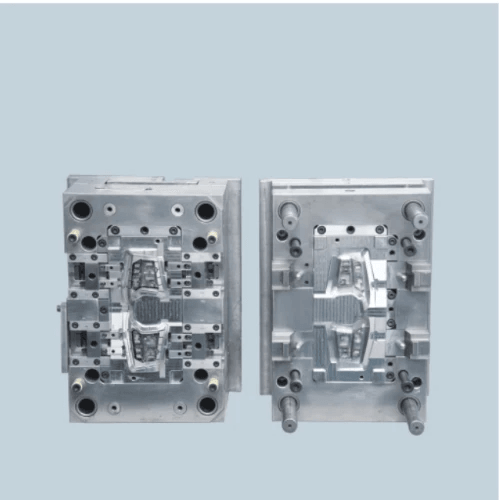
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a mold to create specific shapes and designs. This technique is widely used for producing plastic parts in high volumes, making it an essential method in various industries. When comparing blow molding vs injection molding, it's crucial to understand the unique characteristics and applications of each process.
The Process Explained
The injection molding process begins with heating plastic pellets until they melt into a viscous liquid. This molten plastic is then injected under high pressure into a precisely crafted mold, where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape. One of the key advantages of injection molding is its ability to produce complex geometries with tight tolerances, which can be challenging with other methods like blow molding.
In contrast to blow molding, which typically forms hollow objects, injection molding allows for the creation of solid parts or components with intricate details. This versatility makes it ideal for producing everything from automotive parts to consumer goods. However, it's essential to consider what are the disadvantages of blow molding when deciding on a manufacturing method; sometimes simpler designs may benefit more from this process.
Types of Injection Molding Techniques
There are several types of injection molding techniques that cater to different needs and materials, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages compared to blow molding processes. The most common types include standard injection molding, which focuses on creating solid parts; extrusion blow molding; and injection blow molding.
Extrusion blow molding combines elements from both extrusion and traditional blow molding techniques; it’s particularly useful for producing hollow containers like bottles or tanks efficiently. On the other hand, injection blow molding involves injecting molten plastic into a mold before blowing air inside to form hollow shapes—ideal for creating lightweight containers with precise neck finishes. Understanding these differences helps manufacturers choose the right approach based on their specific requirements.
Common Materials Used in Injection Molding
Injection molded products can be made from various materials, including thermoplastics like polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), and engineering plastics such as polycarbonate (PC) or nylon (PA). These materials are favored for their durability, flexibility, and ability to be molded into intricate designs without compromising structural integrity.
When comparing materials used in blow vs injection molding processes, it's evident that both have unique properties suited for different applications. For instance, while some plastics work exceptionally well in traditional injection molds due to their flow characteristics at high temperatures, others may perform better under conditions typical for extrusion processes like those found in extrusion blow molding or even standard blowing techniques.
Choosing the right material not only affects production efficiency but also influences cost factors associated with both methods—an important consideration when weighing options between blow modeling vs injection modeling cost-wise.
Comparative Cost Analysis
When evaluating the financial implications of blow molding vs injection molding, it's essential to look beyond just the initial investment. Each process has its unique cost structure, influenced by factors such as equipment, materials, and production volume. Understanding these costs is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their manufacturing processes.
Initial Investment vs Production Costs
The initial investment for blow molding equipment can be lower compared to injection molding machines, especially for simpler designs. However, as you delve deeper into production costs, the differences become more pronounced; blow molding typically excels in producing large quantities of hollow parts efficiently and economically. Conversely, injection molding often incurs higher upfront costs due to complex machinery but offers superior precision and versatility in part design.
In terms of operational expenses, blow molding techniques like extrusion blow molding may allow for lower per-unit costs at scale because they are designed specifically for high-volume production. On the flip side, while injection blow molding can be more expensive initially, it often pays off when producing intricate parts that require tight tolerances or specialized features. Ultimately, businesses must weigh these factors carefully when deciding between blow molding vs injection molding.
Maintenance and Operation Expenses
Maintenance is another critical aspect where blow molding vs injection molding diverges significantly. Blow molders generally have fewer moving parts than their injection counterparts, which can lead to reduced maintenance needs and associated costs over time. However, if your operation relies heavily on complex molds or sophisticated machinery in injection molding processes, maintenance expenses could escalate quickly.
Operational expenses also vary based on material usage; while both methods can utilize a range of plastics effectively, the choice between extrusion blow molding and other types may affect overall material waste levels and efficiency during production runs. Additionally, labor costs must be factored into both processes—blow molders often require less skilled labor than those working with intricate injection molds due to their straightforward operation systems. Thus understanding these nuances helps businesses make informed decisions regarding long-term budgeting.
Long-Term Financial Considerations
When contemplating long-term financial implications of each process—blow molding vs injection molding—it’s vital to consider scalability potential alongside market demand fluctuations over time. Blow molded products tend to have lower per-unit costs at larger scales but may lack the design flexibility that some industries demand; hence future product lines could necessitate re-evaluating your chosen method altogether.
On the other hand, while initial investments in injection molds might seem daunting upfront due to their complexity and precision capabilities—they can ultimately lead to significant savings if you anticipate high-volume production of detailed components down the line. Businesses should also keep an eye on evolving technologies; advancements within both sectors could shift cost dynamics dramatically over time.
To summarize this comparative analysis succinctly: understanding how initial investments stack up against ongoing operational expenses—and considering future scalability—is key when choosing between blow modeling vs injection modeling solutions tailored specifically for your business needs.
Production Efficiency

When it comes to production efficiency, understanding the nuances between blow molding vs injection molding can significantly impact your manufacturing decisions. Each process has its strengths and weaknesses that can affect overall productivity and cost-effectiveness. By analyzing cycle times, scalability, and lead times, businesses can make informed choices about which method suits their needs best.
Cycle Times for Each Process
Cycle times are crucial in determining how quickly a product can be manufactured. Blow molding typically has shorter cycle times compared to injection molding, especially when using techniques like extrusion blow molding, which allows for rapid production of hollow parts. However, injection molding might take longer per cycle due to the complexity of the mold design and cooling processes; yet it's important to note that once set up, it can produce intricate designs efficiently.
Understanding what are the disadvantages of blow molding includes recognizing that while it may excel in speed for certain applications, it may not be suitable for all types of products. For instance, if high precision is required or if complex geometries are involved, injection molding often becomes the preferred choice despite its longer cycle times. Ultimately, choosing between these methods hinges on balancing speed with product requirements.
Scalability and Production Volume
Scalability is another essential factor when comparing blow molding vs injection molding techniques. Blow molding is particularly advantageous for producing large volumes of simple shapes like bottles or containers due to its ability to create multiple items simultaneously through processes such as extrusion blow molding or injection blow molding. This makes it a go-to option for manufacturers looking to ramp up production quickly without incurring excessive costs.
On the other hand, while injection molding may have higher initial setup costs due to mold creation and maintenance requirements, it allows for greater flexibility in producing smaller batches with complex designs tailored to specific customer needs. This means that businesses must carefully evaluate their projected production volume against the capabilities of each method before making a decision. In essence, scaling operations effectively requires a clear understanding of both processes' strengths.
Impact on Lead Time
Lead time is directly influenced by both cycle time and scalability in manufacturing processes like blow molding vs injection molding. Generally speaking, because blow molded products can often be produced faster in bulk quantities than injected molded ones, lead times tend to be shorter for simpler items made from blow molds. However, if you need highly detailed parts with intricate designs or tighter tolerances—common considerations when discussing what is the difference between injection molding and other methods—lead time may increase significantly as more setup time is required.
Moreover, factors such as material availability and curing times also play critical roles in determining overall lead time across both processes. While companies might lean towards one technique based on perceived efficiency at first glance; understanding these nuances will ultimately guide them toward better decision-making aligned with their operational goals and customer expectations.
Impact on Product Design

When it comes to product design, the choice between blow molding vs injection molding can significantly influence the outcome. Each process has its own strengths and weaknesses, which can either enable or restrict design possibilities. Understanding these implications is essential for manufacturers aiming to create innovative products that meet market demands.
Design Flexibility in Blow Molding
Blow molding offers remarkable design flexibility, especially suited for creating hollow objects such as bottles and containers. The process allows for various shapes and sizes, accommodating intricate designs without compromising structural integrity. Furthermore, extrusion blow molding and injection blow molding techniques enable manufacturers to incorporate features like handles or spouts seamlessly into their products.
However, what are the disadvantages of blow molding? While it excels in producing lightweight items with consistent wall thickness, it may struggle with complex geometries that require precise detailing. This limitation can pose challenges when designing products that demand high levels of accuracy and detail.
Design Complexity in Injection Molding
This method allows for tight tolerances and the ability to create intricate shapes that are often difficult or impossible to achieve with blow molding. The difference between injection molding and blow molding lies primarily in their capability to handle complexity; injection molds can accommodate undercuts and varying wall thicknesses more effectively than their blow-molded counterparts.
However, this complexity comes at a price—both financially and time-wise—as designing molds for injection processes can be labor-intensive and costly upfront. Additionally, while injection molded parts may offer superior detail, they often require more extensive post-processing compared to simpler blow molded items.
Case Studies on Design Innovations
Several case studies highlight how companies have leveraged both processes for innovative product designs. For instance, a beverage company utilized extrusion blow molding to create uniquely shaped bottles that not only stood out visually but also enhanced grip comfort—definitely a win-win! On the other hand, an automotive manufacturer opted for injection molding to produce lightweight yet robust components with intricate details essential for performance.
These examples illustrate how understanding the nuances of blow molding vs injection molding can lead businesses toward making informed decisions about which method best suits their design needs. As industries continue evolving toward sustainability and efficiency, embracing these innovative approaches will be key in staying competitive within today's fast-paced market landscape.
Conclusion
In the world of manufacturing, the choice between blow molding and injection molding can significantly affect product quality, production efficiency, and overall costs. Understanding the nuances of both processes is crucial for making informed decisions that align with your project needs. As we wrap up our exploration, it’s clear that both methods have unique advantages and drawbacks that must be weighed carefully.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Needs
When considering blow molding vs injection molding, it's essential to evaluate your specific application requirements. Blow molding is ideal for hollow objects like bottles and containers, while injection molding excels in producing complex shapes with tight tolerances. However, one must also consider disadvantages of blow molding, such as limitations in design complexity compared to injection molding's capabilities.
Additionally, understanding what blow molding is used for can guide you toward the right process; if you're creating simple shapes at a high volume, extrusion blow molding may be your best bet. Conversely, if intricate designs are a priority—think gears or custom housings—then injection blow molding could be more suitable. Ultimately, aligning your choice with production goals will help ensure project success.
The Role of Baoyuan in Molding Solutions
Baoyuan has established itself as a leader in providing tailored solutions for both blow and injection molding processes. With expertise in various techniques—including extrusion blow molding and injection blow molding—Baoyuan helps clients navigate the complexities of material selection and process optimization. Their commitment to quality ensures that whether you choose blow or injection methods, you receive products that meet stringent standards.
Furthermore, Baoyuan understands the evolving demands of industries requiring innovative designs and efficient production cycles. By leveraging advanced technology and materials expertise, they empower businesses to make informed decisions about their manufacturing processes—ultimately enhancing productivity while reducing costs associated with mold creation and maintenance expenses.
Future Trends in Blow Molding and Injection Molding
The future of manufacturing is poised to witness exciting advancements in both blow mold versus injection mold technologies. Innovations such as sustainable materials are gaining traction; manufacturers are increasingly exploring eco-friendly options that reduce environmental impact while maintaining product integrity. Additionally, automation technologies are expected to streamline operations further—enhancing cycle times across both processes.
As industries continue to evolve towards customization and rapid prototyping needs, flexibility will become paramount; this trend favors injection over traditional methods due to its ability to accommodate complex designs quickly. In conclusion, staying abreast of these trends will not only inform your decision-making but also position your business competitively within an ever-changing landscape.

