Introduction
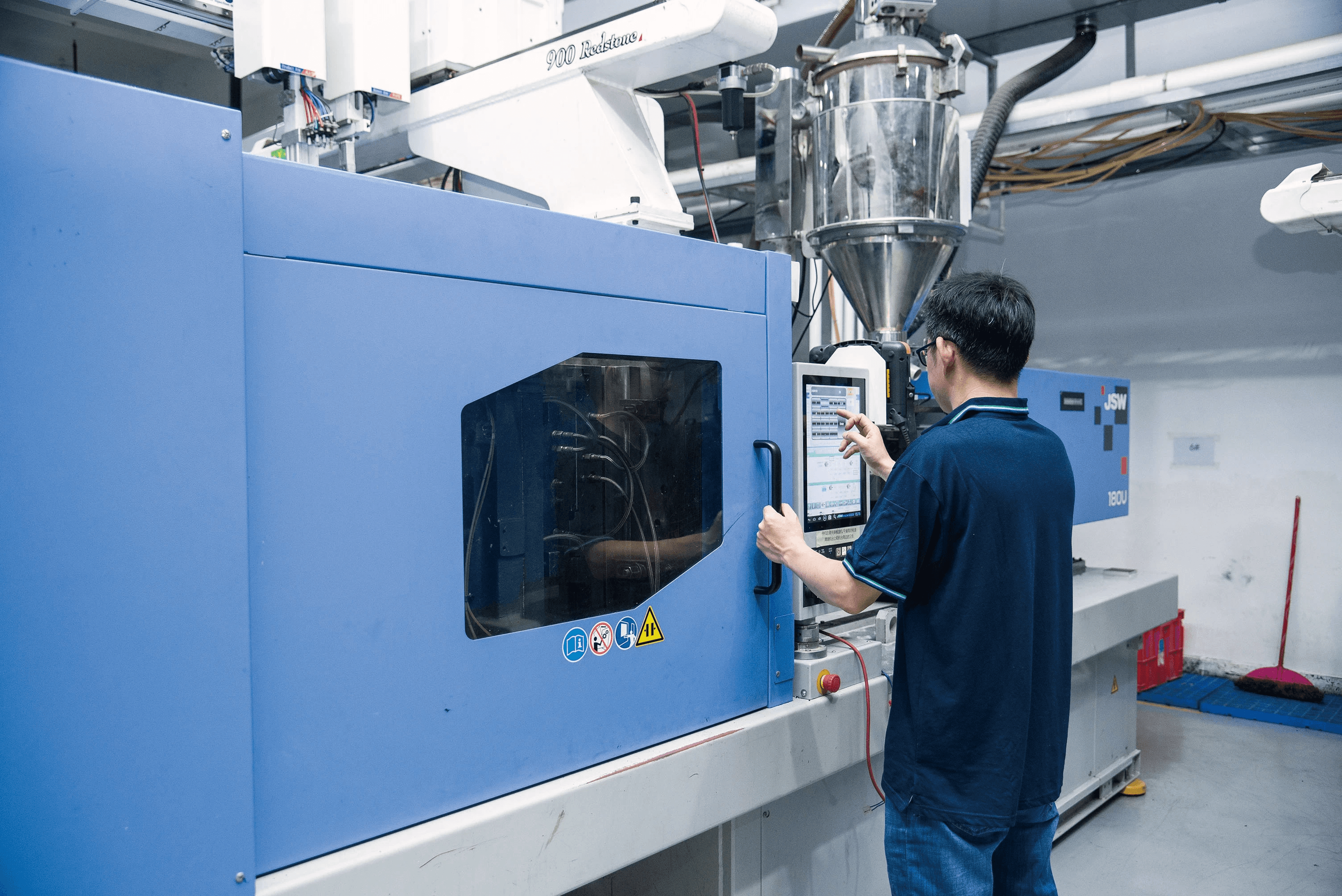
In the world of manufacturing, choosing the right process for creating parts can make all the difference. Urethane casting and injection molding represent two popular methods that cater to various project needs, each with its own set of advantages and limitations. Understanding these processes is crucial for manufacturers looking to optimize production efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Comparing Urethane Casting and Injection Molding
Urethane injection molding offers a flexible approach to part production, allowing for intricate designs and quick turnaround times. On the other hand, traditional injection molding excels in high-volume production runs using injection moldable plastics, making it a staple in many industries. By comparing these methods side by side, manufacturers can determine which process aligns best with their specific requirements.
Why This Guide Matters to Manufacturers
This guide serves as a valuable resource for manufacturers navigating the complexities of urethane casting versus injection molding. With insights into cost factors, design considerations, and quality control measures, it equips decision-makers with essential knowledge to make informed choices. Ultimately, understanding these processes can lead to improved product quality and reduced manufacturing costs.
Key Considerations for Your Project
When embarking on a new project involving plastic for molding, several key considerations come into play. Factors like material selection, production volume, and design flexibility should be weighed carefully to ensure optimal outcomes. By keeping these elements in mind while exploring urethane injection molding or traditional plastic molding options, manufacturers can set themselves up for success.
Understanding Urethane Casting

Urethane casting is a versatile manufacturing process that involves pouring liquid urethane into a mold to create parts and products. This method is distinct from injection molding, where molten plastic is injected into a mold using a plastic injection machine. While both techniques are widely used in the production of plastic components, urethane casting offers unique advantages that can be beneficial for specific applications.
What is Urethane Casting?
Urethane casting utilizes polyurethane resins that cure at room temperature or with heat, allowing for the creation of durable and flexible parts. Unlike injection molding, which relies on high-pressure systems to force materials into molds, urethane casting typically uses lower pressure and can accommodate more intricate designs without the need for complex tooling. This makes it an appealing option for manufacturers looking to produce small to medium-sized runs of custom parts with precise details.
Advantages of Urethane Casting
One of the primary advantages of urethane casting is its cost-effectiveness, especially for low-volume production runs. The tooling costs are significantly lower than those associated with injection molding since molds can be made from softer materials like silicone rather than metal. Additionally, urethane offers excellent flexibility in design; manufacturers can easily adjust formulations to achieve specific properties such as hardness or color without extensive retooling.
Another benefit lies in the rapid prototyping capabilities inherent in urethane casting. Manufacturers can create prototypes quickly and inexpensively compared to traditional methods like mold plastic injection processes used in injection molding services. Furthermore, urethane's excellent resistance to wear and tear makes it suitable for producing durable components across various industries.
Ideal Applications for Urethane
Urethane casting shines in applications requiring intricate designs or specialized properties that might not be achievable through standard injection moldable plastics. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods frequently leverage this technique for producing custom parts like gaskets, seals, and prototypes. Additionally, due to its versatility, urethane is ideal for creating soft-touch surfaces or components that require elasticity—features often sought after by manufacturers aiming to enhance product usability.
Moreover, when speed and flexibility are paramount—such as during product development phases—urethanes provide manufacturers with an agile solution that traditional plastic molding may not offer as readily. Whether it's creating short-run specialty items or functional prototypes designed for rigorous testing environments, urethanes stand out as a reliable choice tailored to meet diverse manufacturing needs.
The Basics of Injection Molding

Injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a mold to create a variety of parts and products. This method is widely used for producing plastic components due to its efficiency and ability to create complex shapes with precision. Understanding the fundamentals of injection molding can help manufacturers make informed decisions when considering their production methods.
What is Injection Molding?
At its core, injection molding is all about transforming raw plastic into finished products through a series of steps involving heating, injecting, and cooling. The process begins with a plastic injection machine that melts down the chosen plastic for molding, which is then injected into a pre-designed mold under high pressure. Once cooled and solidified, the mold opens to release the finished piece—often referred to as an injection moldable plastic component.
This technique allows for mass production of identical parts with remarkable accuracy, making it ideal for industries ranging from automotive to consumer goods. With advancements in technology, today's injection molding services can accommodate various materials beyond traditional plastics, including bio-based and recycled options. This versatility makes it an attractive choice for manufacturers looking to innovate while maintaining efficiency.
Benefits of Injection Molding
One of the standout benefits of injection molding is its ability to produce high volumes of parts quickly and consistently. When compared to urethane injection molding or other methods, this process often results in lower per-unit costs after initial setup due to the speed at which parts can be produced once molds are created. Additionally, the durability and strength of products made from injection moldable plastics are often superior because they undergo rigorous quality control during production.
Another significant advantage lies in design flexibility; intricate designs can be achieved without compromising structural integrity or performance. Manufacturers can also select from a wide range of plastics tailored for specific applications—whether they require high-temperature resistance or enhanced flexibility—ensuring that each project meets precise specifications. Furthermore, modern advancements in 3D printing technology have streamlined prototyping processes before committing to full-scale production runs using traditional plastic molding techniques.
Common Uses for Injection Moldable Plastics
Injection molded plastics find their way into countless applications across numerous industries due to their adaptability and cost-effectiveness. From automotive components like dashboards and bumpers to household items such as containers and toys, these products are integral in daily life yet often go unnoticed until we need them! Medical devices also benefit significantly from this manufacturing process; precision-engineered components ensure reliability in critical applications.
Moreover, electronic housings rely heavily on injection molded parts where durability meets aesthetic appeal—think sleek smartphone cases or robust laptop shells designed with user experience in mind! Even packaging solutions leverage this technology; custom molds produce everything from food containers to cosmetic bottles efficiently while minimizing waste during production cycles. As you explore your own project needs, consider how these common uses align with your goals!
Cost Factors in Each Process
When it comes to choosing between urethane casting and injection molding, understanding the cost factors is crucial for any manufacturer. Both processes can be effective, but their financial implications vary significantly based on materials, tooling, and long-term expenses. Let’s break down these aspects to help you make an informed decision.
Material Costs of Urethane vs. Injection Molding
Material costs are often one of the first considerations when comparing urethane injection molding to traditional injection molding. Urethane materials can be more expensive upfront due to their specialized formulations and properties, which allow for greater flexibility and durability in various applications. In contrast, plastic for molding used in injection processes tends to have lower initial costs, especially when bulk purchasing standard types of injection moldable plastics.
However, while urethane might seem pricier at first glance, its unique characteristics—like resistance to wear and environmental factors—can lead to savings in maintenance and replacement over time. With urethane casting often yielding parts that require less post-processing than those produced with a plastic injection machine, manufacturers may find that overall material costs balance out over the life cycle of the product. Therefore, it’s essential to evaluate not just the initial material prices but also how each option aligns with your project’s specific needs.
Tooling Costs Explained
Tooling costs play a significant role in determining the overall expense of both urethane casting and injection molding processes. For urethane casting, tooling typically involves creating silicone molds that are more affordable than metal molds used for plastic molding processes; this makes it an attractive option for low- to medium-volume production runs. On the other hand, while the upfront investment in tooling for mold plastic injection is higher due to the durability required for metal molds, these molds can produce thousands or even millions of parts before needing replacement.
The trade-off here is clear: if your project demands high volumes with consistent quality over time, investing in robust tooling for injection molding may pay off significantly despite its higher initial costs. Conversely, if you’re looking at shorter runs or prototypes where flexibility is key—urethane casting could save you money upfront without sacrificing quality or performance. Understanding these nuances will help manufacturers choose wisely based on their production goals.
Long-term Cost Perspectives
Long-term cost perspectives are vital when deciding between urethane casting and injection molding services because they encompass not only material and tooling expenses but also operational efficiencies over time. While urethane components might have a higher initial price tag due to material selection and mold creation methods, their longevity can mean fewer replacements or repairs down the line compared to some standard plastic products produced via traditional methods. This durability often leads businesses toward considering total cost ownership rather than just immediate expenditures.
Injection molded parts can achieve economies of scale as production volumes increase; however, they may require additional investments in quality control measures as complexity rises with design intricacies inherent in mold design constraints associated with plastic molding techniques. The critical takeaway here is that evaluating long-term operational expenses alongside immediate costs will provide a clearer picture of which method aligns best with your business strategy moving forward.
Design for Manufacturing (DFM) Considerations
When it comes to manufacturing, design plays a pivotal role in determining the efficiency and effectiveness of the production process. Understanding how design interacts with both urethane casting and injection molding can significantly influence the outcome of your project. This section dives into the nuances of design flexibility in urethane casting, the constraints of injection molding, and essential DFM techniques applicable to both methods.
Design Flexibility in Urethane Casting
Urethane casting offers remarkable design flexibility that allows manufacturers to create complex shapes and intricate details with ease. Unlike traditional plastic molding processes, urethane casting accommodates a variety of design elements without the need for extensive tooling changes. This means you can produce prototypes or small batches with unique features using less time and resources—perfect for those innovative designs that require a bit more creativity.
Additionally, urethane is compatible with various additives that enhance its properties, such as colorants or fillers, enabling manufacturers to tailor their products further. The ability to use different molds for different parts also means you can easily iterate on designs without incurring significant costs. Overall, if you're looking for a method that embraces creative freedom while maintaining quality assurance, urethane casting is hard to beat.
Injection Molding Design Constraints
While injection molding is an incredibly efficient process for mass production, it does come with its own set of design constraints that manufacturers must navigate carefully. For instance, parts designed for mold plastic injection often need to have uniform wall thicknesses; otherwise, issues like warping or incomplete filling may arise during production. This requirement can limit some design choices but ensures consistency across large volumes—a crucial factor when producing injection moldable plastics.
Moreover, draft angles are essential in injection molding to facilitate easy removal from molds without damaging components or the mold itself. These angles add another layer of complexity in designing parts since they dictate how steeply walls must taper towards their base. Understanding these constraints is vital when opting for injection molding services; otherwise, you might end up facing costly redesigns or delays.
Key DFM Techniques for Both Methods
When considering both urethane casting and injection molding processes, certain Design for Manufacturing (DFM) techniques can streamline operations and enhance product quality across the board. First off, simplifying geometry wherever possible will save time during manufacturing while reducing potential defects—something equally applicable whether you're working with urethane or traditional plastic materials like those used in plastic molding projects.
Another critical technique involves thorough communication between designers and engineers early on in the development phase; this collaboration helps identify potential issues before they escalate into costly problems down the line regardless of whether you're utilizing a plastic injection machine or creating custom molds for urethane products. Lastly, implementing effective prototyping methods allows teams to visualize concepts quickly and make necessary adjustments before committing to full-scale production—a best practice worth adopting no matter which manufacturing route you choose.
Quality Control and Production Speed

When it comes to manufacturing processes, quality control and production speed are paramount. Both urethane casting and injection molding offer unique benefits in these areas, but they also come with their own sets of challenges. Understanding how each process handles quality assurance and production efficiency can help manufacturers make informed decisions.
Quality Assurance in Urethane Casting
Quality assurance in urethane casting is a meticulous process that focuses on achieving consistency and precision in every cast. The flexibility of urethane allows for detailed inspection at various stages, ensuring that the final product meets stringent specifications. Moreover, because urethane casting often involves smaller batch sizes, manufacturers can implement more hands-on quality checks compared to larger-scale injection molding operations.
The materials used in urethane casting can be tailored for specific applications, which further enhances the quality control process. This customization means that manufacturers can select the right plastic for molding based on the desired properties—such as hardness or flexibility—thereby improving overall product performance. Additionally, any defects can be identified early due to the slower pace of production compared to high-speed injection molding.
Ultimately, thorough quality assurance practices not only enhance product reliability but also foster customer satisfaction. Manufacturers who prioritize these practices in their urethane injection molding processes are likely to see a positive impact on their reputation and repeat business.
Comparing Production Speed: Urethane vs. Injection
When comparing production speed between urethane casting and injection molding, it's essential to consider both the setup time and cycle time involved in each method. Injection molding typically boasts faster cycle times due to its automated nature; once a mold is created, a plastic injection machine can produce thousands of parts rapidly with minimal downtime.
However, speed isn't everything; it's crucial to weigh it against other factors like setup costs and design complexity. Urethane casting allows for rapid prototyping without extensive tooling investments—ideal for projects needing quick turnaround times or last-minute design changes. On the other hand, while injection moldable plastics excel at mass production efficiency once set up properly, they require significant upfront investment in tooling that may not be justifiable for smaller projects.
In summary, if your project demands high volumes with tight deadlines, injection molding might be your go-to solution; however, if you need flexibility combined with decent speed for lower quantities or prototypes, urethane casting could steal the show.
The Role of Baoyuan in Ensuring Quality
Baoyuan plays a pivotal role in maintaining high standards of quality across both urethane casting and injection molding services offered by various manufacturers. Their commitment to excellence ensures that whether you're utilizing a plastic mold injection service or working with specialized materials like those used in urethane applications—you receive products that meet rigorous industry standards.
By investing heavily in state-of-the-art technology and skilled personnel trained specifically for these processes, Baoyuan helps bridge any gaps between expected outcomes and actual results during manufacturing runs involving either method. This focus on quality not only minimizes waste but also enhances overall efficiency throughout the production lifecycle—from initial design through final inspection.
Moreover, Baoyuan's expertise extends beyond just producing parts; they actively engage with clients throughout every stage of development ensuring that feedback loops are established early on—resulting in better-aligned expectations regarding both timelines and product specifications across all types of plastic for molding applications.
Conclusion
In the grand showdown of urethane casting versus injection molding, choosing the right process for your needs is akin to picking the perfect tool from a toolbox. Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses, tailored to specific project requirements. Understanding not just the basics but also the nuances of urethane injection molding and traditional injection molding will empower manufacturers to make informed decisions that align with their production goals.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Needs
When deciding between urethane casting and injection molding, consider factors such as production volume, design complexity, and material specifications. Urethane is often favored for low-volume runs or prototypes due to its flexibility in design and shorter lead times. On the other hand, if you're looking at large-scale production with consistent quality using injection moldable plastics, then investing in plastic molding might be your best bet.
Balancing Costs and Efficiency
Cost considerations can significantly impact your choice between urethane casting and injection molding services. While initial tooling costs for mold plastic injection can be high, they often pay off in long-term efficiency when producing large quantities. Conversely, urethane offers lower startup costs but may incur higher per-part expenses in high-volume scenarios—striking a balance between upfront investment and operational efficiency is crucial.
The Future of Urethane and Injection Molding
The landscape of manufacturing continues to evolve with advancements in technology impacting both urethane injection molding and traditional methods. Innovations like 3D printing are opening new avenues for producing complex designs that were once only achievable through conventional processes like plastic injection machines or mold plastic injections. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, expect both methods to adapt—potentially integrating more eco-friendly materials into their respective processes.

